
Back جائحة إنفلونزا الخنازير 2009 حسب الدولة Arabic Pandemia de gripe A (H1N1) de 2009-2010 por país y territorio Spanish Vuoden 2009 influenssapandemia maittain Finnish Grippe A (H1N1) de 2009-2010 par pays French 나라별 2009년 인플루엔자 범유행 Korean Pandemia de gripe A de 2009 por continente Portuguese Пандемия свиного гриппа в 2009 году по странам Russian Đại dịch cúm 2009 theo quốc gia Vietnamese 2009年H1N1流感大流行各國疫情及反應 Chinese
This article deals with the status and efforts regarding the 2009 swine flu pandemic by country and continent/region.
| Country | Indicators/ | Cases | Deaths | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spread-Trend/ Intensity/Impact‡ |
Confirmed‡‡ | Confirmed | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ECDC total[1] | 14,378 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reports Total | 6,724,149 | 19,654 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| United States^ | W | = | ** | mod | [2] | (113,690)[3] | 3,433[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brazil | R | - | * | mod | [5] | (58,178)[6] | 2,135[7] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| India | W | + | * | low | [8] | 33,783[9][10] | 2,024[9] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mexico | W | + | ** | mod | [11] | 70,715[12] | 1,316[12] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| China (mainland) | 120,940[13] | 800[14] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turkey | R | + | ** | mod | [15] | 12,316[16] | 656[17] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Argentina | W | - | low | [18] | (11,458)[18] | 626[19] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Russia | W | + | ** | [20][21] | 25,339[22] | 604[22] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| United Kingdom# | R | = | * | [23][24] | (28,456)[25] | 474 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Canada | W | + | ** | [5] | (25,828)[26] | 429[27] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France~ | R | = | * | low | [15] | 1,980,000[28][29] | 344[30] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spain | W | + | * | [15] | (1,538)[31] | 300[32] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Egypt | 15,812[33] | 278[34] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Germany | N | = | low | [35] | (222,360)[36] | 258[36] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| South Korea | W | + | * | low | 107,939[37] | 250[38] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thailand | R | = | * | low | [8] | 31,902[39] | 249[40] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Italy | W | + | ** | [41] | 3,064,933[42] | 244[43] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Colombia | W | + | * | mod | [5] | 4,310[44] | 272[44] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peru | W | - | * | low | [45] | 9,165[46] | 223[19] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ukraine | R | + | ** | mod | [15] | 494[47] | 213[47] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ecuador | W | - | * | low | [5] | 2,251[46] | 200[48] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Japan | W | + | [49] | 11,636[50] | 198[51] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Australia | W | - | [52] | 37,484[29] | 187[53] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poland | W | + | ** | mod | [15] | (2,024)[54] | 181[43] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chile | W | = | low2 | [55] | 12,258[56] | 156[57] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Syria | (452)[58] | 152[58] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greece | N | + | * | [15] | (17,977)[59] | 149[60] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Iran | 3,672[61] | 147[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Venezuela | W | - | * | mod | [5] | 2,187[62] | 135[63] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hungary | L | + | low | [15] | (283)[64] | 134[43] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saudi Arabia | 14,500[61] | 128[61] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Portugal | R | + | * | low | [65] | (166,922)[66] | 122[43] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Romania | W | + | * | mod | [15] | 7,006[67] | 122[67] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Czech Republic | L | + | [15] | 2,445[68] | 102[69] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Israel | W | + | * | low | [15] | 4,330[70] | 94[71] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| South Africa | 12,640[72] | 93[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Malaysia | 12,210[73] | 92[74] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Belarus | W | + | ** | mod | [15] | 88[75] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serbia | R | + | ** | low | [15] | 695[76] | 83[77] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hong Kong | 33,109[78] | 80[79] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cuba | W | + | ** | mod | [80] | 973[81] | 69[82] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Costa Rica | W | - | * | low | [5] | (1,867)[83] | 67[84] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Morocco | 2,890[61] | 64[61] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Netherlands+ | W | + | * | low | [15] | (1,473)[85] | 62[43] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bolivia | W | - | * | low | [5] | 2,310[46] | 59[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vietnam | 11,186[86] | 58[86] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Algeria | 916[72] | 57[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Finland | W | + | ** | [15] | 6,122[87] | 56[88] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Slovakia | S | + | low | [15] | 955[89] | 56[90] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paraguay | L | - | ** | [5] | 855[46] | 54[1][91] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| New Zealand | L | = | * | low | [23] | (3,199)[29] | 50[92][93] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taiwan | (5,474)[94] | 48[95] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sri Lanka | W | + | * | low | [8] | 642[39] | 48[39] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Moldova | 2,524[96] | 46[97] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Palestinian Territories | 1,676[61] | 43[61] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Iraq | 2,880[61] | 42[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Austria | W | + | low | [15] | (964)[98] | 40[43] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulgaria | W | + | *** | [15] | 766[99] | 40[100] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


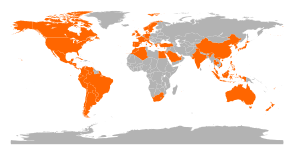


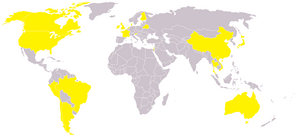
As the pandemic progressed, laboratory testing and confirmation decreased. Confirmed figures for the United Kingdom, in particular, are only meaningful up to 2 July, when routine testing stopped and presumed cases were treated without laboratory confirmation of diagnosis. Following the recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO), many countries stopped issuing estimates of the infected population, making this list inaccurate.
| Pos. | Country | Population[nb 1] | Confirmed cases |
Confirmed cases per 1,000 inhabitants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 306,694 | 8,650 | 28.20 | |
| 2 | 10,414,336 | 214,531[200] | 20.59 | |
| 3 | 10,707,924 | 166,922 | 15.59 | |
| – | 11,870 | 106 | 8.93 | |
| – | 559,846 | 2,625 | 4.68 | |
| – | 7,055,071 | 31,554 | 4.47 | |
| 4 | 46,700,000 | 155,051 | 3.32 | |
| 5 | 2,691,158 | 8,622 | 3.20 | |
| 6 | 338,190 | 972 | 2.87 | |
| – | 91,626 | 234 | 2.55 | |
| 7 | 82,080,000 | 192,348 | 2.34 | |
| 8 | 48,600,000 | 107,939 | 2.22 | |
| 9 | 20,796 | 46 | 2.21 | |
| – | 49,035 | 105 | 2.14 | |
| 10 | 405,165 | 718 | 1.77 | |
| World | 6,790,062,216 | 25,584,595 | 3.76 |
*Includes countries with over 40 confirmed cases only.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: [1] Archived 31 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine Update:"ECDC Daily Update – Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – 19 January 2010" (PDF). 19 January 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 January 2010. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 43 (Oct, 31). WHO PAHO. 9 November 2009. Archived from the original on 18 November 2009. Retrieved 17 November 2009.
- ^ Sum of state reported confirmed cases; see US Swine Flu outbreak table for more information.
- ^ Sum of state reported confirmed deaths in U.S.; see US Swine Flu outbreak table for more information.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 43 (Okt, 31). WHO PAHO. 9 November 2009. Archived from the original on 18 November 2009. Retrieved 17 November 2009.
- ^ Sum of state reported confirmed deaths; see totals in 2009 flu pandemic in Brazil for more information.
- ^ "84 Muertes por gripe y 675 casos graves en 2010". Ansa Latina. 15 July 2010. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Summary of Situation of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Week of 10 Nov – 16 Nov 2009. WHO SEARO. 19 November 2009. Archived from the original on 3 May 2009. Retrieved 21 November 2009.
- ^ a b Ministry of Health; Family Welfare (13 February 2010). "Consolidated Status of Influenza A H1N1". Press Information Bureau. Archived from the original on 14 February 2010. Retrieved 13 February 2010.
- ^ Ministry of Health; Family Welfare (12 July 2010). "Consolidated Status(Weekly) of Influenza A H1N1". Press Information Bureau. Archived from the original on 25 July 2010. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 40 (Okt, 10). WHO PAHO. 16 October 2009. Archived from the original on 16 October 2009. Retrieved 19 October 2009.
- ^ a b "Influenza A(H1N1 )" (in Spanish). México, Secretaría de Salud. 18 January 2010. Archived from the original on 28 January 2010. Retrieved 18 January 2010.
- ^ Productions, Visible. (31 January 2011) News on Yahoo! Health Archived 9 June 2024 at the Wayback Machine. Health.yahoo.com. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ China reports 7 A/H1N1 flu deaths in March Archived 24 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af "EuroFlu – Weekly Electronic Bulletin". Data Status Week 45 (Nov, 8). WHO/Europe. 13 November 2009. Archived from the original on 19 November 2009. Retrieved 18 November 2009.
- ^ "A/H1N1 flu death toll rises to 19 in Turkey: ministry". Xinhua. 5 November 2009. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 5 November 2009.
- ^ toute l'info suisse romande :: votre multi-portails régional Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Romandie. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b Ministry of Health (18 December 2009). "Influenze Pandémica (H1N1) 2009. República Argentina" (PDF). week 49 (in Spanish). Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 November 2011. Retrieved 22 December 2009.
- ^ a b c d e Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Archived 14 February 2011 at the Wayback Machine (19 April 2010 – 17 h GMT; 12 h EST)]
- ^ A combination of two sources:
Spread/Intensanity from: "EuroFlu – Weekly Electronic Bulletin". Data Status Week 45 (Nov, 8). WHO/Europe. 13 November 2009. Archived from the original on 19 November 2009. Retrieved 18 November 2009.
Trend from: "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 74". Data Status Week 44 (Nov, 1). WHO. 13 November 2009. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 18 November 2009. - ^ Northwest: L= / * ; Central: S= / * ; South: S= / * ; Volga: S= / * ; Urals: S+ / * ; Siberian:S= / * ; Far East R+ / * ; Source: EuroFlu week 42
- ^ a b Russia[user-generated source]
- ^ a b c "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 74". Data Status Week 44 (Nov, 1). WHO. 13 November 2009. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 18 November 2009.
- ^ England: W= / * , North Ireland: S- / ** , Scotland: L= / * , Wales: W+ / *. Source: EuroFlu week 45 (Wales: EuroFlu week 45, Scotland: EuroFlu week 45)
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "HPA Weekly National Influenza Report". Week 01. UK HPA. 8 January 2010. Archived from the original on 29 August 2011. Retrieved 9 January 2010.
- ^ Canada, Public Health Agency of (19 October 2018). "Flu (influenza): FluWatch surveillance". www.canada.ca. Archived from the original on 29 August 2022. Retrieved 29 August 2022.
- ^ 2009–2010 FluWatch: February 28 to March 6, 2010 (Week 9) Archived 19 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Phac-aspc.gc.ca (12 March 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Situation en France" (in French). Groupe régionaux d'observatoire de la grippe. 18 November 2009. Archived from the original on 24 November 2009. Retrieved 18 November 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p "WHO South Pacific – Pandemic Influenza A / H1N1 2009 Surveillance". Pacific Public Health Surveillance Network. 21 December 2009. Archived from the original on 14 December 2009. Retrieved 26 December 2009.
- ^ "Institut de veille sanitaire". Invs.sante.fr. Archived from the original on 12 April 2010. Retrieved 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Informe diario de situación Nacional e Internacional. Gripe A/H1N1". 23 July 2009. Archived from the original on 14 December 2009. Retrieved 16 December 2009.
- ^ Trinidad Jiménez: 'La gripe A afectó a casi el 30% de la población española' – Sociedad – La Opinión A Coruña Archived 16 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Laopinioncoruna.es. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ Ministry of Health, [2] Archived 20 August 2010 at the Wayback Machine| Updated 13 February 2010
- ^ Ministry Of Health Archived 20 August 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Mohp.gov.eg. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "EuroFlu – Weekly Electronic Bulletin". Archived from the original on 16 April 2014. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ a b RKI (Arbeitsgemeinschaft Influenza) Archived 11 October 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Influenza.rki.de. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "S. Korea vows to go all out to curb flu spread". Yonhap News. 3 November 2009. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 3 November 2009.
- ^ INSIDE JoongAng Daily Archived 7 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Joongangdaily.joins.com (6 April 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 in SAE Region". WHO SEARO. 18 February 2010. Archived from the original on 3 May 2009. Retrieved 22 February 2010.
- ^ H1N1 FLU:สธ.เผยหวัด 09 คร่าชีวิตคนไทยอีก 2 ราย ยอดสะสมขยับเป็น 249 ราย Archived 7 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Ryt9.com (26 August 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b "EuroFlu – Weekly Electronic Bulletin". Data Status Week 44 (Nov, 1). WHO/Europe. 6 November 2009. Archived from the original on 19 November 2009. Retrieved 18 November 2009.
- ^ "Influenza A/H1N1 – Il punto della situazione" (in Italian). 26 November 2009. Archived from the original on 27 November 2009. Retrieved 27 November 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Archive: Number of fatal cases Archived 15 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Ecdc.europa.eu (3 May 2010). Retrieved on 8 February 2011.
- ^ a b Ministerio de Protección Social (1 September 2010). "ANÁLISIS DE LA PANDEMIA DE INFLUENZA A H1N1 COMPARATIVO 2009 – 2010" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 March 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
- ^ "Informe Regional DIRESA Callao" (PDF). Data Status Week 40 (Okt, 10). WHO PAHO. 16 October 2009. Retrieved 19 October 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". WHO PAHO. 9 November 2009. Archived from the original on 18 November 2009. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- ^ a b "Best Practices Reporting". 15 December 2009. Archived from the original on 27 July 2011. Retrieved 20 December 2009.
- ^ "Confirmadas 200 muertes por la gripe A en Ecuador". La Hora. Quito. ECE. 18 May 2010. Retrieved 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 73". Data Status Week 43 (Okt, 25). WHO. 6 November 2009. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 18 November 2009.
- ^ "Chugai Pharma to Triple Tamiflu Supply in Japan". Bloomberg. 7 September 2009. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 7 September 2009.
- ^ Masayuki Takata; Hideki Hiramoto (17 April 2010), "Now is the time to rethink new flu tack", The Daily Yomiuri, Japan, Daily Yomiuri Online, archived from the original on 18 April 2010
- ^ A combination of two sources:
Spread from: "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 68". Data Status Week 38 (Sep, 20). WHO. 2 October 2009. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 20 October 2009.
Trend from: "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 69". Data Status Week 39 (Sep, 27). WHO. 9 October 2009. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 20 October 2009. - ^ "PANDEMIC (H1N1) 2009 UPDATE BULLETIN" (PDF), Pandemic (H1N1) Influenza 2009, no. 1200 AEST on 30 October 2009, Australia: Department of Health and Ageing, 30 October 2009, archived (PDF) from the original on 11 April 2013, retrieved 26 January 2013
- ^ "A/H1N1 flu takes more lives in Poland". 15 December 2009. Archived from the original on 9 January 2010. Retrieved 15 December 2009.
- ^ "Reporte sobre Influenza". Ministerio de Salud de Chile (in Spanish). 4 November 2009. Archived from the original on 22 November 2009. Retrieved 17 November 2009.
- ^ "Influenza Pandémica (H1N1) 2009" (PDF). Ministerio de Salud de Chile. 4 November 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 November 2009. Retrieved 16 November 2009.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Archived 8 February 2011 at the Wayback Machine (6 July 2010 – 17 h GMT; 12 h EST)", Pan American Health Organization
- ^ a b "Syria confirms two new deaths of A/H1N1 flu". Xinhua (27 January 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Ο αριθμός των νεκρών λόγω γρίπης συνεχώς αυξάνεται" (in Greek). 26 February 2009. Archived from the original on 2 March 2010. Retrieved 28 February 2009.
- ^ Weekly influenza surveillance overview 7 May 2010 Archived 26 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Main surveillance developments in week 17/2010 (26 April 2010 – 2 May 2010)
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "Latest situation in the Region". WHO EMRO. 5 January 2010. Archived from the original on 14 March 2010. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
- ^ Noticias de Prensa Latina Archived 8 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Prensa-latina.cu (1 January 1970). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ (in Spanish) Pagina no encontrada | Diario El Carabobeño Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. El-carabobeno.com. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "A/H1N1 flu virus claims 4th victim in Hungary". Xinhua. 16 October 2009. Archived from the original on 17 October 2009. Retrieved 16 October 2009.
- ^ a b A combination of two sources:
Spread/Trend/Intensity from: "EuroFlu – Weekly Electronic Bulletin". Data Status Week 45 (Nov, 8). WHO/Europe. 13 November 2009. Archived from the original on 19 November 2009. Retrieved 18 November 2009.
Impact from: "EuroFlu – Weekly Electronic Bulletin". Data Status Week 42 (Okt, 18). WHO/Europe. 23 October 2009. Archived from the original on 19 November 2009. Retrieved 18 November 2009. - ^ "156.701 casos confirmados em Portugal". Portal da Saúde. Ministério da Saúde. Archived from the original on 27 February 2012. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ a b "Date statistice privind gripa nouă", Comunicate de presă (Press Release) (in Romanian), Romania: MINISTERUL SĂNĂTĂŢII, 4 September 2009, archived from the original on 4 March 2016, retrieved 26 January 2013
- ^ "Swine flu claims 101 lives in ČR, low demand for vaccination". Prague Daily Monitor. 25 February 2010. Archived from the original on 25 February 2010.
- ^ "ČR among EU countries with highest swine flu death rate". Prague Daily Monitor. 19 March 2010. Archived from the original on 29 March 2010.
- ^ "Swine-Flu Infection Count at 4,330". Arutz Sheva. 26 October 2009. Archived from the original on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 26 October 2009.
- ^ 15-year-old with pre-existing illness dies of swine flu – Israel News, Ynetnews Archived 7 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Ynetnews.com (20 June 1995). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 in the African Region: Update 75". WHO Regional Office for Africa. 17 March 2010. Archived from the original on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 19 March 2010.
- ^ "Malaysia on alert for new A/H1N1 wave". Xinhua. 4 December 2009. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 4 December 2009.
- ^ Positive H1N1 Cases Increase From August 1 To 7 Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Bernama (11 August 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ В прошлом году в реанимациях Минска от пневмонии и свиного гриппа умерло 123 человека — Новости OPEN.BY Archived 17 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine. News.open.by. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ У Србији до сада вакцинисано 148.226 особа Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Влада Републике Србије
- ^ "Novi udar gripa?". Glas javnosti. Archived from the original on 14 April 2010. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ a b Daily "Swine and Seasonal Flu Monitor – Volume 1, Number 13" (PDF). Surveillance and Epidemiology Branch, Centre for Health Protection. 17 December 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 19 December 2009.
- ^ Hong Kong influenza A/H1N1 death toll rises to 80 – People's Daily Online Archived 16 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine. English.people.com.cn (15 April 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 41 (Okt, 17). WHO PAHO. 26 October 2009. Archived from the original on 28 October 2009. Retrieved 29 October 2009.
- ^ Raul Castro confirms 41st swine flu death | Other Countries | Archived 6 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine. En.trend.az (21 December 2009). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Cuba reporta 69 fallecidos por el virus A (H1N1)". Cubanet.org. 16 June 2010. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ 100 personas con gripe A en el último mes Archived 9 June 2024 at the Wayback Machine. LaRepublica.net. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ Suma Costa Rica 15 muertes por virus A(H1N1) Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Spanish.peopledaily.com.cn (16 July 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d e "ECDC Daily Update – Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – 28 September 2009" (PDF). 28 September 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 October 2009. Retrieved 28 September 2009.
- ^ a b "Death toll from A/H1N1 influenza rises to 58 in Vietnam". Xinhua (10 February 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Finland to vaccinate entire population against A/H1N1 flu". Xinhua. 26 November 2009. Archived from the original on 29 November 2009. Retrieved 26 November 2009.
- ^ "Weekly influenza surveillance overview - 13 August 2010 | Main surveillance developments in Weeks 30–31 2010 (26 July 2010 – 8 August 2010)" (PDF). European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 April 2017. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ Slovakia Document Store / Panorama.sk – Pravda Daily on Saturday, December 19 Archived 1 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Panorama.sk. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ Weekly influenza surveillance overview 16 April 2010 Archived 16 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Main surveillance developments in week 14/2010 (5 April 2010 – 11 April 2010)
- ^ Noticias de Prensa Latina Archived 8 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Prensa-latina.cu (1 January 1970). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ Radio New Zealand : News : National : Swine flu death toll revised to 35 Archived 1 May 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Radionz.co.nz (28 April 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Pandemic Influenza H1N1 2009 (swine flu) – Update 203". New Zealand Ministry of Health. 26 August 2010. Archived from the original on 19 November 2010. Retrieved 7 February 2011.
- ^ "174 H1N1 hospitalized cases in Taiwan: health officials". eTaiwanNews. 10 September 2009. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 10 September 2009.
- ^ Microsoft Word – Taiwan_Influenza_Express[Engl]2010_W33.doc. (PDF) . Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ ИА "Новости – Молдова" Archived 11 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Newsmoldova.ru (28 January 2011). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ Www.Basa.Md Archived 26 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Www.Basa.Md. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "First local swine flu death reported in Austria". monstersandcritics.com. 10 November 2009. Archived from the original on 26 November 2009. Retrieved 10 November 2009.
- ^ "ИНФОРМАЦИЯ ОТ НАЦИОНАЛНАТА РЕФЕРЕНТНА ЛАБОРАТОРИЯ ПО ГРИП И ОСТРИ РЕСПИРАТОРНИ ЗАБОЛЯВАНИЯ НА НЦЗПБ". The Sofia Echo. 9 November 2009. Archived from the original on 30 March 2010. Retrieved 10 November 2009.
- ^ a b Weekly influenza surveillance overview 5 February 2010 Archived 26 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Main surveillance developments in week 4/2010 (25 Jan 2010—31 Jan 2010)
- ^ Expanding access to healthcare for people with low incomes Archived 13 December 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Ministry of Health of the Republic of Latvia, 2 February 2011
- ^ Weekly influenza surveillance overview 19 February 2010 Archived 16 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Main surveillance developments in week 06/2010 (8 Feb 2010—14 Feb 2010)
- ^ Al-Mahrezi, Abdulaziz; Samir, Nafisa; Al-Zakwani, Ibrahim; Al-Maharmi, Zakaria; Balkhair, Abdulla; Al-Shafee, Mohammed (23 April 2012). "Clinical characteristics of influenza A H1N1 versus other influenza-like illnesses amongst outpatients attending a university health center in Oman". International Journal of Infectious Diseases. 16 (7): E504–E507. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2012.02.015. PMID 22521779. Archived from the original on 5 December 2022. Retrieved 5 December 2022.
- ^ Department of Communicable Disease Surveillance & Control (25 August 2010). Influenza A(H1N1)2009 Pandemic Response, An Overview (Report). Sultanate of Oman Ministry of Health. p. 29. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 5 December 2022.
- ^ Google Translate. Translate.google.com. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ В Грузии от свиного гриппа скончался 33-й больной – свиной грипп, Грузия – Новости Кавказа – Росбалт Archived 2 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Rosbalt.ru. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ Asciende a 30 número de salvadoreños fallecidos por A/H1N1 Archived 26 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Sdpnoticias.com. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". WHO PAHO. 11 September 2009. Archived from the original on 11 September 2009. Retrieved 12 September 2009.
- ^ "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 60". Data Status Week 30 (Jul, 26). WHO. 7 August 2009. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 29 September 2009.
- ^ "Over 5,000 H1N1 infections in RP". abs-cbnNews. 26 October 2009. Archived from the original on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 26 October 2009.
- ^ Search | Sun.Star Network Online[permanent dead link]. Sunstar.com.ph (31 August 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ Saba Net – Yemen news agency Archived 16 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Sabanews.net. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ الصالح: 19 ألفاً تطعَّموا ضد إنفلونزا الخنازير و64 ألفاً ضد الموسمية. Al-Jarida (in Arabic). Kuwait. 5 January 2010. Archived from the original on 23 October 2010. Retrieved 7 February 2011.
- ^ The UB Post-Mongolia's Independent English Newspaper – H1N1 Mongolian Update Archived 22 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Ubpost.mongolnews.mn (15 January 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Mongolian protestors demand health minister resign". Reuters. 11 March 2010. Archived from the original on 9 March 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ "Ukentlig Rapport" (in Norwegian). Public Health Institute. 16 December 2009. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 16 December 2009.
- ^ Google Translate. Translate.google.com (26 January 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Surveillance Report". Health Protection Surveillance Centre. 5 November 2009. Archived from the original on 8 November 2009. Retrieved 6 November 2009.
- ^ "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 63". Data Status Week 33 (Aug, 16). WHO. 28 August 2009. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 29 September 2009.
- ^ "A/H1N1 flu virus claims third victim in Macedonia". Xinhua. 29 November 2009. Archived from the original on 30 November 2009. Retrieved 29 November 2009.
- ^ Swine flu death toll reaches 26 in Macedonia Archived 25 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Idividi. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Gripa uzrokovana novim virusom A/H1N1" (in Croatian). HZJZ. 16 December 2009. Archived from the original on 21 December 2009. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- ^ "Swine flu killed 24 people". DAWN. 27 January 2010. Archived from the original on 28 February 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ Individual.com Archived 3 November 2023 at the Wayback Machine. Individual.com. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "6 Muertos en el año por gripe a/H1N1 en Guatemala". Ansa Latina. 3 January 2010. Archived from the original on 21 October 2010. Retrieved 7 February 2011.
- ^ "70 cadets quarantined for swine flu". Baltic Reports. 4 November 2009. Archived from the original on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 10 November 2009.
- ^ Weekly influenza surveillance overview 26 February 2010 Archived 26 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Main surveillance developments in week 7/2010 (15 February 2010 – 21 February 2010)
- ^ "Situational Update of Cases". Ministry of Health, Singapore. 7 July 2009. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 8 July 2009.
- ^ "Boy, 5, dies from H1N1". Straits Times. Archived from the original on 1 March 2010.
- ^ "Ülemiste hingamisteede viirusnakkused ja gripp 51. nädalal" (in Estonian). Tervisekaitseinspektsioon (Estonian Health Protection Inspectorate). 23 December 2009. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 24 December 2009.
- ^ Seagripp nĂľudis Eestis 21. ohvri – DELFI Archived 29 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Delfi.ee. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Communiqué de Presse, 2009-11-19" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 February 2012. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ "Mexicaanse griep treft 40.000 Belgen in een week, twee doden" (in Dutch). hbvl.be. 29 October 2009. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 29 October 2009.
- ^ 16th swine flu fatality recorded Archived 12 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Jordan Times (17 December 2009). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Število obolelih strmo narašča, proti pandemski gripi cepljenih več kot 32.000 ljudi". Inštitut za varovanje zdravja RS. 26 November 2009. Archived from the original on 3 December 2009. Retrieved 26 November 2009.
- ^ "Bundesamt f r Gesundheit – Grippe A(H1N1)". Archived from the original on 14 May 2009. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ Swine flu pandemic said to be on its last breath – swissinfo. Swissinfo.ch. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 39 (Okt, 03). WHO PAHO. 16 October 2009. Archived from the original on 16 October 2009. Retrieved 19 October 2009.
- ^ Doctora sospechosa de "gripe porcina" Archived 2 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine. LaTribuna.hn (19 March 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "A/H1N1 kills 17 in Afghanistan". Xinhua. 12 December 2009. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 12 December 2009.
- ^ "Kosovo reports third swine flu death". SETimes. 24 November 2009. Archived from the original on 27 November 2009. Retrieved 24 November 2009.
- ^ "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 60". Data Status Week 29 (July, 19). World Health Organization. 31 July 2009. Archived from the original on 5 August 2009. Retrieved 5 August 2009.
- ^ Google Translate Archived 9 June 2024 at the Wayback Machine. Translate.google.com. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ Google Translate Archived 9 June 2024 at the Wayback Machine. Translate.google.com. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b c "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 42 (Okt, 24). WHO PAHO. 9 November 2009. Archived from the original on 18 November 2009. Retrieved 17 November 2009.
- ^ Noticias de Prensa Latina. Prensa-latina.cu (1 January 1970). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ Albania confirms 6th swine flu death Archived 14 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine. SETimes.com (21 December 2009). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ A/H1N1, tjeter viktime nga virusi / Archived 26 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Top-channel.tv. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Pandemic H1N1 2009". WHO SEARO. 27 September 2009. Archived from the original on 3 May 2009. Retrieved 16 October 2009.
- ^ "Qatar to get H1N1 vaccine in November". Peninsula Daily. 4 October 2009. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 9 October 2009.
- ^ "Eighth death from swine flu". Cyprus Mail. 23 January 2010. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 7 February 2011.
- ^ North Korea Today – Good Friends: North Korea Today No. 311/No.311-1 Hot Topics December 2009 Archived 6 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Goodfriendsusa.blogspot.com (8 December 2009). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "SKorean president offers swine flu aid to NKorea". The San Diego Union Tribune. Associated Press. 7 December 2009. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 38 (Sep, 26). WHO PAHO. 9 October 2009. Archived from the original on 9 October 2009. Retrieved 12 October 2009.
- ^ Seventh H1N1 death recorded – News Archived 1 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Go-Jamaica (29 December 2009). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 71". Data Status Week 41 (Okt, 11). WHO. 23 October 2009. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 25 October 2009.
- ^ toute l'info suisse romande :: votre multi-portails régional Archived 5 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Romandie. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ Cambodian A/H1N1 death case rises to 6_English_Xinhua. Xinhua (18 December 2009). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d "SITUATION REPORT Pandemic influenza (H1N1) 2009" (PDF). ECDC. 9 August 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 February 2010. Retrieved 27 September 2009.
- ^ a b "EuroFlu – Weekly Electronic Bulletin". Data Status Week 43 (Okt, 25). WHO/Europe. 30 October 2009. Archived from the original on 19 November 2009. Retrieved 18 November 2009.
- ^ a b "Weekly influenza surveillance overview" (PDF). ECDC. 30 October 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 November 2009. Retrieved 31 October 2009.
- ^ Fifth swine flu death Archived 6 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine. timesofmalta.com (14 July 2009). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 30 (August, 1). WHO PAHO. 28 August 2009. Retrieved 1 September 2009.
- ^ Sudan confirms 5 A/H1N1 flu deaths, 145 infection cases_English_Xinhua. Xinhua (28 December 2009). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 40 (Okt, 10). WHO PAHO. 26 October 2009. Archived from the original on 28 October 2009. Retrieved 29 October 2009.
- ^ Ghana, Business Advice, Jobs, News, Business Directory, Real Estate, Finance, Forms, Auto Archived 9 June 2024 at the Wayback Machine. BusinessGhana (21 June 2010). Retrieved on 8 February 2011.
- ^ Armenia records A/H1N1 decline – Health – Panorama | Armenian news Archived 29 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Panorama.am. Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Fréttir" [News]. Landlæknisembættið [Directorate of Health] (in Icelandic). 12 November 2009. Archived from the original on 2 March 2012.
- ^ "Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 67". Data Status Week 37 (Sep, 13). WHO. 25 September 2009. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009. Retrieved 29 September 2009.
- ^ "H1N1: 121 Cases In Nine Days, 27 School Classes Advised To Close". BruDirect.com. 19 August 2009. Archived from the original on 22 August 2009. Retrieved 19 August 2009.
- ^ Second Death From H1N1 | Third Stories Archived 25 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Brudirect.com (6 April 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ a b "Suriname And Belize To Begin H1N1 Flu Vaccination". News.brunei.fm. Nam New Network. 19 February 2010. Archived from the original on 26 February 2012. Retrieved 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 39 (Okt, 03). WHO PAHO. 9 October 2009. Archived from the original on 9 October 2009. Retrieved 12 October 2009.
- ^ "A/H1N1 flu cases increase to 242 in Laos". Xinhua. 26 August 2009. Archived from the original on 9 August 2011. Retrieved 26 August 2009.
- ^ Swine flu death reported in Bermuda – Bermuda Sun... Beyond the Headlines – Hamilton, Bermuda Archived 5 April 2023 at the Wayback Machine. Bermudasun.bm (6 January 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "Swine flu cases rises in Zimbabwe". Afrique Jet. 20 October 2009. Archived from the original on 27 October 2012. Retrieved 6 November 2009.
- ^ "Zambia: Copperbelt Records Highest Swine Flu Cases". AllAfrica. 1 October 2009. Archived from the original on 16 October 2009. Retrieved 1 October 2009.
- ^ "Excess flu jabs could go abroad". BBC News. 15 January 2010. Archived from the original on 12 April 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ "H1N1 cases reach 91". Bhutan Observer. 11 June 2010.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". WHO PAHO. 4 September 2009. Archived from the original on 11 September 2009. Retrieved 14 September 2009.
- ^ Cameroon Launches Massive Swine Flu Vaccine Campaign | Africa | English Archived 9 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Voanews.com (29 October 2010). Retrieved on 7 February 2011.
- ^ "EuroFlu – Weekly Electronic Bulletin". Data Status Week 40 (Okt, 4). WHO/Europe. 9 October 2009. Archived from the original on 5 November 2009. Retrieved 20 October 2009.
- ^ "Confirmed swine flu cases rise to 61 in Kyrgyzstan". Trend.az. 20 November 2009. Archived from the original on 23 November 2009. Retrieved 20 November 2009.
- ^ "Tíðindaskriv" (PDF). landslaeknin.fo. 7 September 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 23 November 2009.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 33 (August, 22). WHO PAHO. 28 August 2009. Archived from the original on 5 February 2010. Retrieved 1 September 2009.
- ^ "Number of A/H1N1 cases explodes". The Monaco Times. 16 November 2009. Archived from the original on 18 November 2009. Retrieved 13 December 2009.
- ^ "No Swine Flu deaths in Botswana". Mmegi Online. 26 September 2009. Archived from the original on 13 May 2011. Retrieved 26 September 2009.
- ^ "Guyana confirms 27th H1N1 case". Guyana Chronicle. 31 December 2009. Archived from the original on 9 June 2024. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- ^ "Regional Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Data Status Week 28 (July, 18). WHO PAHO. 28 August 2009. Retrieved 1 September 2009.
- ^ "Number of swine flu cases reaches 16 in Tajikistan". 18 December 2009. Retrieved 18 December 2009.
- ^ "Azerbaijan reports new case of swine flu". APA. 11 November 2009. Archived from the original on 14 November 2009. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- ^ "Summary of Situation of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Week of 21 Sep – 27 Sep 2009. WHO SEARO. 27 September 2009. Archived from the original on 3 May 2009. Retrieved 16 October 2009.
- ^ "Influenza A: i casi salgono a 5. Tutti verso la guarigione". San Marino RTV. 10 November 2009. Archived from the original on 5 September 2012. Retrieved 8 December 2009.
- ^ "E600 to test for swine flu". Times of Swaziland. 27 August 2009. Archived from the original on 22 May 2013. Retrieved 27 August 2009.
- ^ "Swine flu hits Greenland as toll rises in Europe". Focus Information Agency. 11 November 2009. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- ^ "Situation updates – Influenza A(H1N1)". Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response. World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 13 May 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2009.
- ^ "Human infection with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus: updated interim WHO guidance on global surveillance" (PDF). Annex 4. WHO. 10 July 2009. p. 16. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 August 2009. Retrieved 25 July 2009.
- ^ Dawood FS, Jain S, Finelli L, et al. (June 2009). "Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans". N. Engl. J. Med. 360 (25): 2605–15. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0903810. PMID 19423869.
the number of confirmed cases is an underestimate of the number of cases that have occurred
- ^ CDC (12 March 2009). "Questions and Answers Regarding Estimating Deaths from Influenza in the United States". CDC. Archived from the original on 1 December 2009. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ "Crisisbeheer Mexicaanse griep opgeheven". De Morgen (in Flemish). 25 March 2010. Archived from the original on 25 January 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
Cite error: There are <ref group=nb> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=nb}} template (see the help page).
