
Back أدينوسين أحادي الفوسفات Arabic آدنوزین مونوفوسفات AZB Аденозинмонофосфат Bulgarian Adenozin-monofosfat BS Monofosfat d'adenosina Catalan Adenosinmonofosfát Czech Adenosinmonofosfat Danish Adenosinmonophosphat German Μονοφωσφορική αδενοσίνη Greek Adenosín monofosfato Spanish
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (February 2013) |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
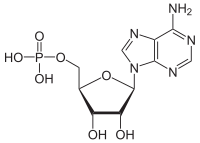
5′-Adenylic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names
Adenosine 5'-monophosphate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.455 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Adenosine+monophosphate |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14N5O7P | |
| Molar mass | 347.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Density | 2.32 g/mL |
| Melting point | 178 to 185 °C (352 to 365 °F; 451 to 458 K) |
| Boiling point | 798.5 °C (1,469.3 °F; 1,071.7 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.9[citation needed], 3.8, 6.1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine.[1] As a substituent it takes the form of the prefix adenylyl-.[2]
AMP plays an important role in many cellular metabolic processes, being interconverted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP), as well as allosterically activating enzymes such as myophosphorylase-b. AMP is also a component in the synthesis of RNA.[3] AMP is present in all known forms of life.[4]
- ^ "Adenosine monophosphate (Compound)". PubChem. NCBI. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ^ "Nomenclature of Carbohydrates: (Recommendations 1996)". Journal of Carbohydrate Chemistry. 16 (8): 1191–1280. 1997. doi:10.1080/07328309708005748.
- ^ Jauker M, Griesser H, Richert C (November 2015). "Spontaneous Formation of RNA Strands, Peptidyl RNA, and Cofactors". Angewandte Chemie. 54 (48): 14564–9. doi:10.1002/anie.201506593. PMC 4678511. PMID 26435376.
- ^ "Adenosine monophosphate". The Human Metabolome Database. Retrieved 3 July 2020.