
Back لعب (ميكانيك) Arabic Vůle (technika) Czech Slør (mekanik) Danish Spiel (Technik) German Lõtk Estonian Jeu (mécanique) French Gioco (meccanica) Italian バックラッシュ (機械) Japanese 백래시 (공학) Korean Speling Dutch
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2010) |
In mechanical engineering, backlash, sometimes called lash, play, or slop, is a clearance or lost motion in a mechanism caused by gaps between the parts. It can be defined as "the maximum distance or angle through which any part of a mechanical system may be moved in one direction without applying appreciable force or motion to the next part in mechanical sequence."[1]p. 1-8 An example, in the context of gears and gear trains, is the amount of clearance between mated gear teeth. It can be seen when the direction of movement is reversed and the slack or lost motion is taken up before the reversal of motion is complete. It can be heard from the railway couplings when a train reverses direction. Another example is in a valve train with mechanical tappets, where a certain range of lash is necessary for the valves to work properly.
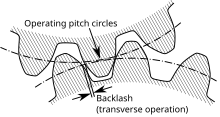
Depending on the application, backlash may or may not be desirable. Some amount of backlash is unavoidable in nearly all reversing mechanical couplings, although its effects can be negated or compensated for. In many applications, the theoretical ideal would be zero backlash, but in actual practice some backlash must be allowed to prevent jamming.[citation needed] Reasons for specifying a requirement for backlash include allowing for lubrication, manufacturing errors, deflection under load, and thermal expansion.[citation needed] A principal cause of undesired backlash is wear.
- ^ Bagad, V.S. (2009). Mechatronics (4th revised ed.). Pune: Technical Publications. ISBN 9788184314908. Retrieved 28 June 2014.