
Back سيفيم Arabic سفم Persian Céphem French Cefem Croatian セフェム Japanese 세펨 Korean Cefemy Polish Cefemi Slovenian Цефами Ukrainian 头孢烯 Chinese
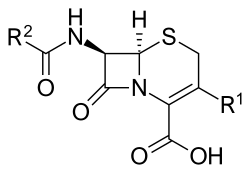

Cephems are a sub-group of β-lactam antibiotics including cephalosporins and cephamycins.[1] It is one of the most common 4-membered ring heterocycle.[2] Produced by actinomycetes, cephamycins were found to display antibacterial activity against a wide range of bacteria, including those resistant to penicillin and cephalosporins.[3] The antimicrobial properties of Cephem include the attachment to certain penicillin-binding proteins that are involved in the production of cell walls of bacteria.[4]
- ^ Hamilton-Miller JM (November 2003). "Chemical and microbiologic aspects of penems, a distinct class of beta-lactams: focus on faropenem". Pharmacotherapy. 23 (11): 1497–1507. doi:10.1592/phco.23.14.1497.31937. PMID 14620395. S2CID 43705118.
- ^ Vitaku E, Smith DT, Njardarson JT (December 2014). "Analysis of the structural diversity, substitution patterns, and frequency of nitrogen heterocycles among U.S. FDA approved pharmaceuticals". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 57 (24): 10257–10274. doi:10.1021/jm501100b. PMID 25255204.
- ^ Stapley EO, Jackson M, Hernandez S, Zimmerman SB, Currie SA, Mochales S, et al. (September 1972). "Cephamycins, a new family of beta-lactam antibiotics. I. Production by actinomycetes, including Streptomyces lactamdurans sp. n". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2 (3): 122–131. doi:10.1128/AAC.2.3.122. PMC 444278. PMID 4790552.
- ^ Molteni E, Onida G, Ceccarelli M, Cappellini G (2021-04-03). "Ab Initio Spectroscopic Investigation of Pharmacologically Relevant Chiral Molecules: The Cases of Avibactam, Cephems, and Idelalisib as Benchmarks for Antibiotics and Anticancer Drugs". Symmetry. 13 (4): 601. Bibcode:2021Symm...13..601M. doi:10.3390/sym13040601. hdl:2434/831526. ISSN 2073-8994.