
Back استقطاب دائري Arabic Polarització circular Catalan Zirkularpolarisation German Polarización circular Spanish Polarisation circulaire French קיטוב מעגלי HE 원편파 Korean Круговая поляризация Russian Krožna polarizacija Slovenian โพลาไรเซชันแบบวงกลม Thai
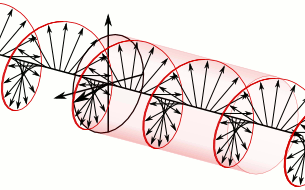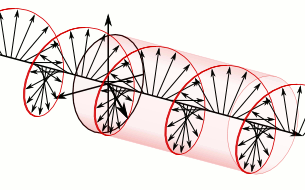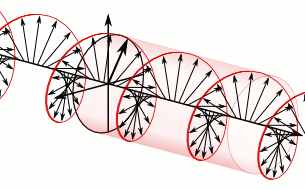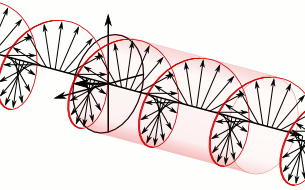
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
In electrodynamics, the strength and direction of an electric field is defined by its electric field vector. In the case of a circularly polarized wave, the tip of the electric field vector, at a given point in space, relates to the phase of the light as it travels through time and space. At any instant of time, the electric field vector of the wave indicates a point on a helix oriented along the direction of propagation. A circularly polarized wave can rotate in one of two possible senses: right-handed circular polarization (RHCP) in which the electric field vector rotates in a right-hand sense with respect to the direction of propagation, and left-handed circular polarization (LHCP) in which the vector rotates in a left-hand sense.
Circular polarization is a limiting case of elliptical polarization. The other special case is the easier-to-understand linear polarization. All three terms were coined by Augustin-Jean Fresnel, in a memoir read to the French Academy of Sciences on 9 December 1822.[1][2] Fresnel had first described the case of circular polarization, without yet naming it, in 1821.[3]
The phenomenon of polarization arises as a consequence of the fact that light behaves as a two-dimensional transverse wave.
Circular polarization occurs when the two orthogonal electric field component vectors are of equal magnitude and are out of phase by exactly 90°, or one-quarter wavelength.
- ^ A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel, vol. 1 (1866), pp. 731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", Zenodo: 4745976, 2021 (open access); §§9–10.
- ^ Académie des Sciences, Procès-verbaux des séances de l'Académie tenues depuis la fondation de l'Institut jusqu'au mois d'août 1835, vol. 7 (for 1820–23), Hendaye, Basses Pyrénées: Imprimerie de l'Observatoire d'Abbadia, 1916, p. 401.
- ^ A. Fresnel, "Note sur le calcul des teintes que la polarisation développe dans les lames cristallisées" et seq., Annales de Chimie et de Physique, Ser. 2, vol. 17, pp. 102–11 (May 1821), 167–96 (June 1821), 312–15 ("Postscript", July 1821); reprinted (with added section nos.) in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel, vol. 1 (1866), pp. 609–48; translated as "On the calculation of the tints that polarization develops in crystalline plates, & postscript", Zenodo: 4058004 (Creative Commons), 2021; author's footnote to §16.