
Back Dreadnought (Schiff, 1879) German HMS Dreadnought (1875) Spanish اچاماس دریدنوت (۱۸۷۵) Persian HMS Dreadnought (1875) Finnish HMS Dreadnought (1875) French ドレッドノート (装甲艦) Japanese HMS Dreadnought (1875) Ukrainian
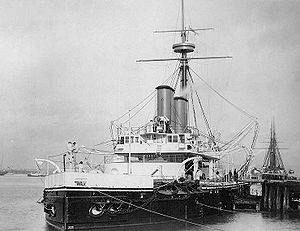 Bow view of Dreadnought, probably after 1894
| |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Operators | |
| Preceded by | Devastation class |
| Succeeded by | HMS Inflexible |
| Completed | 1 |
| Scrapped | 1 |
| History | |
| Name | Dreadnought |
| Ordered | 1870 Naval Programme |
| Builder | Pembroke Dockyard |
| Way number | No. 2 |
| Laid down | 10 September 1870 |
| Launched | 8 March 1875 |
| Completed | 15 February 1879 |
| Commissioned | 1884 |
| Out of service | 1905 |
| Reclassified | As second-class battleship, 1900 |
| Fate | Sold for scrap, 14 July 1908 |
| General characteristics (as built) | |
| Type | Ironclad turret ship |
| Displacement | 10,886 long tons (11,061 t) |
| Length | 320 ft (97.5 m) (pp) *343 ft (105 m) (oa) |
| Beam | 63 ft 10 in (19.5 m) |
| Draught | 26 ft 6 in (8.1 m) |
| Installed power | 8,206 ihp (6,119 kW); 12 cylindrical boilers |
| Propulsion | 2 shafts; 2 compound-expansion steam engines |
| Speed | 14 knots (26 km/h; 16 mph) |
| Range | 5,700 nmi (10,600 km; 6,600 mi) @ 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Complement | 369 |
| Armament | 4 × 12.5 in (320 mm) rifled muzzle-loading guns |
| Armour |
|
HMS Dreadnought was an ironclad turret ship built for the Royal Navy during the 1870s. Construction was halted less than a year after it began and she was redesigned to improve her stability and buoyancy. Upon completion in 1879, the ship was placed in reserve until she was commissioned in 1884 for service with the Mediterranean Fleet. Upon her return 10 years later, she became a coast guard ship in Ireland for two years. The ship then became a depot ship in 1897 before she was reclassified as a second-class battleship in 1900. Dreadnought participated in the annual fleet manoeuvres for the next two years before she became a training ship in 1902. The ship was taken out of service three years later and sold for scrap in 1908.