
Back الشق الطولي Arabic Cissura interhemisfèrica Catalan Fissura longitudinalis cerebri German Fesùra longitudinèla EML Cisura interhemisférica Spanish Hemisferioarteko arteka Basque Scissure longitudinale French Scissura interemisferica Italian 大脳縦裂 Japanese Fissura longitudinalis cerebri NN
| Longitudinal fissure | |
|---|---|
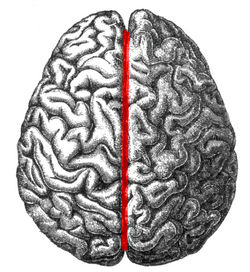 The human brain as viewed from above. Median longitudinal fissure visible in red, running top to bottom. | |
 Longitudinal fissure shown in red (animation) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fissura longitudinalis cerebri, fissura cerebri longitudinalis |
| NeuroNames | 35 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_4041 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.007 |
| TA2 | 5417 |
| FMA | 83727 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The longitudinal fissure (or cerebral fissure, great longitudinal fissure, median longitudinal fissure, interhemispheric fissure) is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continuation of the dura mater (one of the meninges) called the falx cerebri.[1] The inner surfaces of the two hemispheres are convoluted by gyri and sulci just as is the outer surface of the brain.
- ^ "longitudinal fissure - Ontology Browser - Rat Genome Database". rgd.mcw.edu. Retrieved 2019-09-24.