
Back سبارفلوكساسين Arabic Sparfflocsacin Welsh Esparfloxacino Spanish اسپارفلوکساسین Persian Sparfloksasiini Finnish Sparfloxacine French Sparfloxacina Italian Sparfloksacyna Polish Sparfloxacină Romanian Спарфлоксацин Russian
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | spar FLOX a sin |
| Trade names | Spacin, Zagam, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a600002 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 92% |
| Protein binding | 45% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic glucuronidation Cytochrome P450 system not involved |
| Elimination half-life | 16 to 30 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal (50%) and renal (50%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.238 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
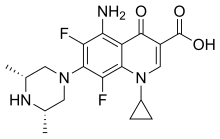
| Formula | C19H22F2N4O3 |
| Molar mass | 392.407 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 266 to 269 °C (511 to 516 °F) (dec.) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Sparfloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections. It has a controversial safety profile.[1]
It was patented in 1985 and approved for medical use in 1993.[2] Zagam is no longer available in the United States.
- ^ Psaty BM (December 2008). "Clinical trial design and selected drug safety issues for antibiotics used to treat community-acquired pneumonia". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 47 (Suppl 3): S176–S179. doi:10.1086/591400. PMC 2587028. PMID 18986285.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 501. ISBN 9783527607495.