Back ثيازول Arabic Tiazol Azerbaijani تیازول AZB Тыазол Byelorussian Tiazole Catalan Thiazol Czech Thiazol German Tiazolo Esperanto Tiazol Spanish Tiazol Basque
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Thiazole | |||
| Other names
Thiazole
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.475 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H3NS | |||
| Molar mass | 85.12 g·mol−1 | ||
| Boiling point | 116 to 118 °C (241 to 244 °F; 389 to 391 K) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.5 (of conjugate acid) [1] | ||
| -50.55·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
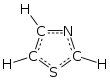
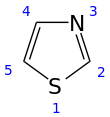
Thiazole (/ˈθaɪ.əzoʊl/), or 1,3-thiazole, is a 5-membered heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen. The term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS.[2] The thiazole ring is notable as a component of the vitamin thiamine (B1).
- ^ Zoltewicz, J. A.; Deady, L. W. (1978). "Quaternization of Heteroaromatic Compounds: Quantitative Aspects". Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry Volume 22. Vol. 22. pp. 71–121. doi:10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60103-8. ISBN 9780120206223.
- ^ Eicher, T.; Hauptmann, S. (2003). The Chemistry of Heterocycles: Structure, Reactions, Syntheses, and Applications. Wiley. ISBN 978-3-527-30720-3.