
Back Immuunstelsel Afrikaans Immunsystem ALS Sistema immunitario AN جهاز مناعي Arabic جهاز مناعى ARZ প্ৰতিৰোধ তন্ত্ৰ Assamese Sistema inmunitariu AST İmmun sistemi Azerbaijani باغیشیقلیق سیستمی AZB Иммунлыҡ системаһы Bashkir
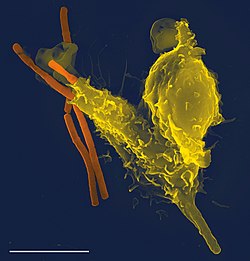
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions.
Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against viral infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial peptides called defensins, and the complement system. Jawed vertebrates, including humans, have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms, including the ability to adapt to recognize pathogens more efficiently. Adaptive (or acquired) immunity creates an immunological memory leading to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that same pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.
Dysfunction of the immune system can cause autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cancer. Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. In humans, immunodeficiency can be the result of a genetic disease such as severe combined immunodeficiency, acquired conditions such as HIV/AIDS, or the use of immunosuppressive medication. Autoimmunity results from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system.