
Back Аелементқәа рпериодикатә система Abkhazian Periodieke tabel Afrikaans Periodensystem ALS የንጥረ ነገሮች ሠንጠረዥ Amharic Tabla periodica d'os elementos AN आवर्त सारणी ANP الجدول الدوري Arabic طابلو دوري ARY جدول دورى ARZ পৰ্যাবৃত্ত তালিকা Assamese
| Part of a series on the |
| Periodic table |
|---|
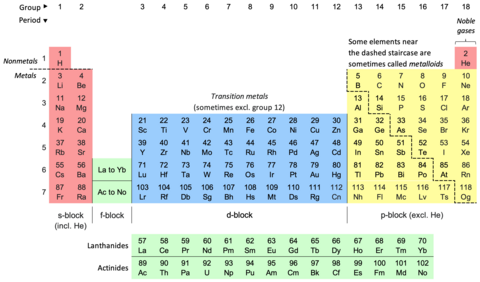
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows ("periods") and columns ("groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics.
Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and decreases from left to right across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right.
The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as a dependence of chemical properties on atomic mass. As not all elements were then known, there were gaps in his periodic table, and Mendeleev successfully used the periodic law to predict some properties of some of the missing elements. The periodic law was recognized as a fundamental discovery in the late 19th century. It was explained early in the 20th century, with the discovery of atomic numbers and associated pioneering work in quantum mechanics, both ideas serving to illuminate the internal structure of the atom. A recognisably modern form of the table was reached in 1945 with Glenn T. Seaborg's discovery that the actinides were in fact f-block rather than d-block elements. The periodic table and law are now a central and indispensable part of modern chemistry.
The periodic table continues to evolve with the progress of science. In nature, only elements up to atomic number 94 exist;[a] to go further, it was necessary to synthesise new elements in the laboratory. Today, while all the first 118 elements are known, thereby completing the first seven rows of the table, chemical characterisation is still needed for the heaviest elements to confirm that their properties match their positions. It is not yet known how far the table will go beyond these seven rows; moreover, theoretical calculations suggest that this unknown region will not follow the patterns of the known part of the table. Some scientific discussion also continues regarding whether some elements are correctly positioned in today's table. Many alternative representations of the periodic law exist, and there is some discussion as to whether there is an optimal form of the periodic table.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).