
Back دهن عديد اللاتشبع Arabic ފެޓް (ޕޮލީއަންސެޗުރޭޓެޑް ފެޓް) DV چربی غیراشباع چندگانه Persian Lemak tak jenuh ganda ID Lemak politaktepu Malay Gordura poli-insaturada Portuguese Polinezasićena mast Serbo-Croatian Polyunsaturated fat SIMPLE Polinezasićena mast Serbian Fleromättat fett Swedish
| Types of fats in food |
|---|
| Components |
| Manufactured fats |
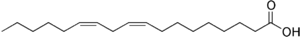
In biochemistry and nutrition, a polyunsaturated fat is a fat that contains a polyunsaturated fatty acid (abbreviated PUFA), which is a subclass of fatty acid characterized by a backbone with two or more carbon–carbon double bonds.[1][2] Some polyunsaturated fatty acids are essentials. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are precursors to and are derived from polyunsaturated fats, which include drying oils.[3]


- ^ "Essential Fatty Acids". Micronutrient Information Center, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR. May 2014. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- ^ "Omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil, alpha-linolenic acid". Mayo Clinic. 2017. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- ^ Anneken, David J.; Both, Sabine; Christoph, Ralf; Fieg, Georg; Steinberner, Udo; Westfechtel, Alfred (2006). "Fatty Acids". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_245.pub2. ISBN 3527306730.