
Back عدد كمي Arabic Númberu cuánticu AST Квантавы лік Byelorussian Квантово число Bulgarian কোয়ান্টাম সংখ্যা Bengali/Bangla Kvantni broj BS Nombre quàntic Catalan Kvantové číslo Czech Квантла хисеп CV Quantenzahl German
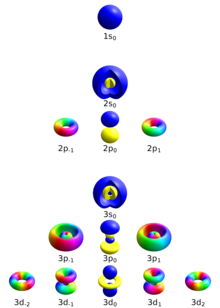
| Part of a series of articles about |
| Quantum mechanics |
|---|
In quantum physics and chemistry, quantum numbers are quantities that characterize the possible states of the system. Quantum numbers are closely related to eigenvalues of observables. When the corresponding observable commutes with the Hamiltonian, the quantum number is said to be "good", and acts as a constant of motion in the quantum dynamics.
To fully specify the state of the electron in a hydrogen atom, four quantum numbers are needed. The traditional set of quantum numbers includes the principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin quantum numbers. To describe other systems, different quantum numbers are required. For subatomic particles, one needs to introduce new quantum numbers, such as the flavour of quarks, which have no classical correspondence.
