| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 66.1%[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 County Results
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in New York State |
|---|
 |
The 1932 United States presidential election in New York took place on November 8, 1932. All contemporary 48 states were part of the 1932 United States presidential election. Voters chose 47 electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.
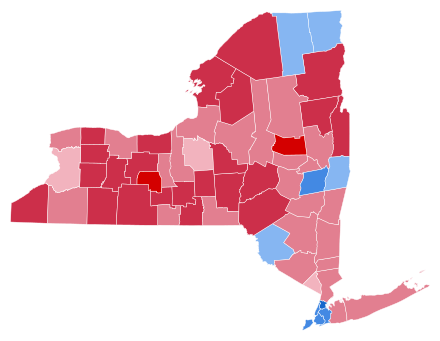
New York was won by Democratic Governor of New York Franklin D. Roosevelt, who was challenging embattled incumbent Republican President Herbert Hoover. Roosevelt ran with Speaker of the House John Nance Garner of Texas, and Hoover ran with incumbent Vice President Charles Curtis of Kansas. With the incumbent Republican president greatly weakened by his failures to adequately address the Great Depression, the New York Governor easily carried his home state in the midst of a nationwide Democratic landslide. Franklin Roosevelt took 54.07% of the vote in New York State versus Herbert Hoover's 41.33%, a margin of 12.74%. Socialist candidate Norman Thomas finished a distant third, with 3.78%. Although, despite being Roosevelt's home state – and although he won the state comfortably – in the context of the 1932 nationwide Democratic landslide, New York weighed in for this election as 5% more Republican than the national average.
The presidential election of 1932 was a partisan election, with more than 95.4% of the electorate casting votes for either the Democratic Party or the Republican.[2]
1932 was the first time a Democrat had won New York's electoral votes since 1912, when Republican vote-splitting for the third party candidacy of Theodore Roosevelt had allowed Democrat Woodrow Wilson to win the state with a plurality of only 41% of the vote. Franklin Roosevelt's 54.07% made him the first Democratic presidential candidate to win an absolute majority of the vote in New York State since Samuel J. Tilden in 1876. Roosevelt's 12.74% victory margin over Hoover was the widest victory margin ever for a Democratic presidential candidate in New York State up to that point, although it would be surpassed just 4 years later by Roosevelt's own 20-point re-election victory in 1936.
Roosevelt's support in the state did not appear spontaneously in 1932; his winning strategy in New York State was primarily to build upon the Democratic coalition fellow New Yorker Al Smith had organized behind him in the 1928 election. Smith had narrowly lost the state in the midst of a nationwide Republican landslide, but had dramatically improved upon how Democrats before him had done, and laid the groundwork for turning the state Democratic in 1932 and beyond. In 1920 and 1924, Republicans had swept every county in New York State and Democrats took less than 30% of the vote. In 1928, Smith came within 2 points of winning the state by sweeping all five boroughs of heavily populated New York City, winning Albany County, home to the state capital of Albany, along with neighboring Rensselaer County, and winning two counties in northern New York along the Saint Lawrence River, Clinton County and Franklin County. FDR turned a 2-point statewide Democratic defeat in 1928 into a 13-point victory in 1932 primarily by pushing up turnout and victory margins in Smith's 1928 counties, as the county map remained almost entirely the same. Only one county in New York State actually changed hands from Hoover in 1928 to Roosevelt in 1932, rural Sullivan County, which voted Democratic for the first time since 1912.
- ^ Bicentennial Edition: Historical Statistics of the United States, Colonial Times to 1970, part 2, p. 1072.
- ^ "1932 Presidential General Election Results – New York". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved July 25, 2013.


