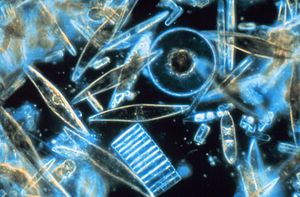
Biogenic silica (bSi), also referred to as opal, biogenic opal, or amorphous opaline silica, forms one of the most widespread biogenic minerals. For example, microscopic particles of silica called phytoliths can be found in grasses and other plants.
Silica is an amorphous metalloid oxide formed by complex inorganic polymerization processes. This is opposed to the other major biogenic minerals, comprising carbonate and phosphate, which occur in nature as crystalline iono-covalent solids (e.g. salts) whose precipitation is dictated by solubility equilibria.[1] Chemically, bSi is hydrated silica (SiO2·nH2O), which is essential to many plants and animals.
Diatoms in both fresh and salt water extract dissolved silica from the water to use as a component of their cell walls. Likewise, some holoplanktonic protozoa (Radiolaria), some sponges, and some plants (leaf phytoliths) use silicon as a structural material. Silicon is known to be required by chicks and rats for growth and skeletal development. Silicon is in human connective tissues, bones, teeth, skin, eyes, glands and organs.
- ^ Coradin, T., Lopez, P.J. (2003). "Biogenic Silica Patterning: Simple Chemistry or Subtle Biology?" ChemBioChem 3: 1-9.
