
Back الجمعية الاتحادية الروسية Arabic Asamblea Federal de Rusia AST Федераль йыйылыш Bashkir Федэральны Сход Расіі Byelorussian Федерално събрание на Русия Bulgarian Холбооной Суглаан BXR Assemblea Federal de Rússia Catalan Российн Федерацин Федералан Гулам CE Federální shromáždění (Rusko) Czech Федераци пуçтарăнăвĕ CV
Federal Assembly Федеральное Собрание Federalnoye Sobraniye | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | • Federation Council • State Duma |
| History | |
| Founded | 12 December 1993 |
| Preceded by | Supreme Soviet of Russia Constitutional Conference of Russia |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | State Duma: 450 Federation Council: 170 |
 | |
Federation Council political groups | Political parties (167)
Vacant (2)
|
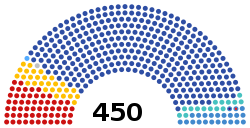 | |
State Duma political groups | Government (324)
Other parties (125)
|
| Elections | |
| Parallel voting | |
Last Federation Council election | 12 December 1993 |
Last State Duma election | 17–19 September 2021 |
Next State Duma election | Before 20 September 2026 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Federation Council Building, Moscow | |
 | |
| State Duma Building, Moscow | |
| Website | |
| Gov.ru | |
| Constitution | |
| Constitution of Russia, Chapter V, Articles 94-109 | |
The Federal Assembly[a] is the national legislature of the Russian Federation. The upper house is the Federation Council, and the lower house is the State Duma. The assembly was established by the Constitution of the Russian Federation in 1993, replacing the former Supreme Soviet of Russia. It is located in Moscow.
The Chairman of the Federation Council is the third most important position after the President and the Prime Minister. In the case that both the President and the Prime Minister are incapacitated, the Chairman of the upper house of the Russian parliament becomes Acting President of Russia.[1][2] The assembly replaced
The jurisdiction of the State Duma includes: consent to the appointment of the Chairman of the Government, deciding the issue of confidence in the Government, appointment and dismissal of the Chairman of the Central Bank, appointment and dismissal of the Chairman and half of the auditors of the Accounting Chamber, appointment and dismissal of the Commissioner for Human Rights, proclamation of amnesty, advancing of charges against the President for his impeachment and others.[3]
The jurisdiction of the Council of the Federation includes: approval of changes in borders between subjects of the Russian Federation, approval of the decree of the President on the introduction of a martial law or on the introduction of a state of emergency, deciding on the possibility of using the Armed Forces of Russia outside the territory of Russia, appointment of elections of the President, impeachment of the President, appointment of judges of higher courts of Russia, appointment and dismissal of the Procurator-General of the Russian Federation, appointment and dismissal of Deputy Chairman and half of the auditors of the all Accounting Chamber and others.[4]
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ "Пост Председателя Совета Федерации РФ – это третий пост в стране. В случае недееспособности президента и премьера именно председатель верхней палаты парламента должен возглавить государство."
- ^ "Почему у нас третье лицо в государстве Председатель Совета Федерации? Потому что это федерация, он не распускается, он действует постоянно." - Сергей Шахрай
- ^ The Constitution of the Russian Federation. Article 103
- ^ The Constitution of the Russian Federation. Article 102