
Back Tataramon na Sambal BCL Sambal-ngṳ̄ CDO Idioma zambal Spanish Tinà Sambal jezik Croatian Bahasa Sambal ID Pagsasao a Sambal ILO 삼발어 Korean Język sambal Polish Lenga sambal, tinà PMS Língua sambal Portuguese
This article should specify the language of its non-English content, using {{lang}}, {{transliteration}} for transliterated languages, and {{IPA}} for phonetic transcriptions, with an appropriate ISO 639 code. Wikipedia's multilingual support templates may also be used. (May 2019) |
| Sambal | |
|---|---|
| Sambali | |
| Native to | Philippines |
| Region | Zambales, Pangasinan, Metro Manila, Palawan |
| Ethnicity | Sambal |
Native speakers | 70,000 (2000)[1] |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | Philippines (as a regional language) |
| Regulated by | Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | xsb |
| Glottolog | tina1248 |
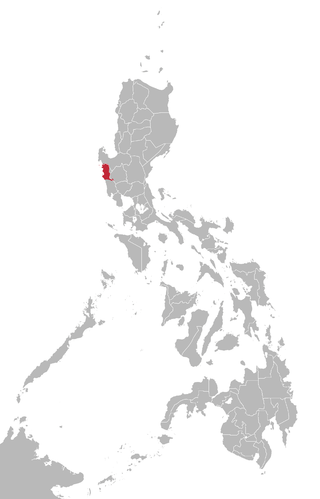 Area where Sambal is spoken | |
Sambal or Sambali is a Sambalic language spoken primarily in the Zambal municipalities of Santa Cruz, Candelaria, Masinloc, Palauig, and Iba, in the Pangasinense municipality of Infanta, and areas of Pampanga in the boundary with Zambales in the Philippines; speakers can also be found in Panitian, Quezon, Palawan and Barangay Mandaragat or Buncag of Puerto Princesa.[citation needed] The speakers of the language are decreasing due to the fact that many of the speakers are shifting to Tagalog & Ilocano.
The first European-produced reference grammar of any indigenous language of the Philippines was that of Zambal, published circa 1601.[2]
- ^ Sambal at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ^ Mojarro Romero, Jorge (2022-05-03). "The Spanish Friars and Philippine Languages". Manila Times.