
Back إعادة شراء الأسهم Arabic Zpětný odkup akcií Czech بازخرید سهام Persian Rachat d'actions par l'entreprise French Athcheannach stoic Irish רכישה עצמית HE 자사주재매입 Korean Inkoop van eigen aandelen Dutch Buy back Polish Обратный выкуп Russian
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2024) |
The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (October 2018) |
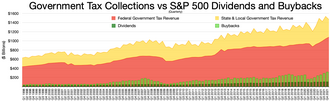
State tax revenue
Federal tax revenue
S&P 500 Stock buyback
S&P 500 Dividends
Share repurchase, also known as share buyback or stock buyback, is the reacquisition by a company of its own shares.[1] It represents an alternate and more flexible way (relative to dividends) of returning money to shareholders.[2] When used in coordination with increased corporate leverage, buybacks can increase share prices.[3]
In most countries, a corporation can repurchase its own stock by distributing cash to existing shareholders in exchange for a fraction of the company's outstanding equity; that is, cash is exchanged for a reduction in the number of shares outstanding. The company either retires the repurchased shares or keeps them as treasury stock, available for reissuance.
Under U.S. corporate law, there are six primary methods of stock repurchase: open market, private negotiations, repurchase "put" rights, two variants of self-tender repurchase (a fixed price tender offer and a Dutch auction), and accelerate repurchases.[4] More than 95% of the buyback programs worldwide are through an open-market method,[2] whereby the company announces the buyback program and then repurchases shares in the open market (stock exchange). In the late 20th and the early 21st century, there was a sharp rise in the volume of share repurchases in the United States: US$5 billion in 1980 rose to US$349 billion in 2005. Large share repurchases started later in Europe than in the United States, but are nowadays a common practice around the world.[5]
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) rule 10b-18 sets requirements for stock repurchase in the United States.[6] Rule 10b-18 provides a voluntary "safe harbor" from liability for market manipulation under Sections 9(a)(2) and 10(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.[7]
- ^ "Share Repurchase Definition". Investopedia.
- ^ a b Fernandes, Nuno (2014). Finance for executives: a practical guide for managers. NPV Publishing. ISBN 978-989-98854-0-0. OCLC 878598064.
- ^ "How share buybacks and cheap debt are used to boost stock prices". Banking Observer. Retrieved 4 Sep 2022.
- ^ "Accelerated Share Repurchase (ASR)".
- ^ For evidence of the increased use of share repurchases, see Bagwell, Laurie Simon and John Shoven, "Cash Distributions to Shareholders" 1989, Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 3 No. 3, Summer, 129–140.
- ^ "Rule 10b-18". Investopedia. Retrieved 10 Apr 2014.
- ^ "SEC.gov | Division of Trading and Markets:Answers to Frequently Asked Questions Concerning Rule 10b-18 ("Safe Harbor" for Issuer Repurchases)". www.sec.gov. Retrieved 2024-03-09.