Back Joego-Slawië Afrikaans Jugoslawien ALS ዩጎስላቪያ Amharic Geugoslafia ANG يوغوسلافيا Arabic يوݣوسلاڤيا ARY يوجوسلاڤيا ARZ Yugoslavia AST Yuqoslaviya Azerbaijani Югославия Bashkir
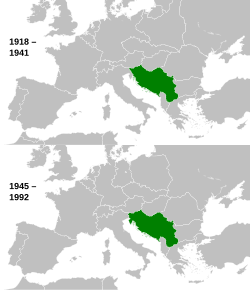
Yugoslavia[a] (/ˌjuːɡoʊˈslɑːviə/; lit. 'Land of the South Slavs') was a country in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 to 1992.
It came into existence in 1918[b] following World War I, under the name of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes from the merger of the Kingdom of Serbia with the provisional State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (which was formed from territories of the former Austria-Hungary), and constituted the first union of South Slavic peoples as a sovereign state, following centuries of foreign rule over the region under the Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary. Peter I of Serbia was its first sovereign. The kingdom gained international recognition on 13 July 1922 at the Conference of Ambassadors in Paris.[7] The official name of the state was changed to Kingdom of Yugoslavia on 3 October 1929.
The Kingdom was invaded by the Axis powers on 6 April 1941. In 1943, a Democratic Federal Yugoslavia was proclaimed by the Partisan resistance. In 1944, King Peter II, then living in exile, recognised it as the legitimate government. After a communist government was elected in November 1945, the monarchy was abolished, and the country was renamed the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia. It acquired the territories of Istria, Rijeka, and Zadar from Italy. Partisan leader Josip Broz Tito ruled the country from 1944 as prime minister and later as president until his death in 1980. In 1963, the country was renamed for the final time, as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY).
The six constituent republics that made up the SFRY were the socialist republics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia. The Socialist Republic of Serbia contained two socialist autonomous provinces, Kosovo and Vojvodina, which after 1974 were largely equal to the other members of the federation.[8][9] After an economic and political crisis in the 1980s and the rise of nationalism and ethnic conflicts, Yugoslavia broke up along its republics' borders, at first into five countries, leading to the Yugoslav Wars. From 1993 to 2017, the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia tried political and military leaders from the former Yugoslavia for war crimes, genocide, and other crimes committed during those wars.
After the breakup, the republics of Montenegro and Serbia formed a reduced federative state, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) (known from 2003 to 2006 as Serbia and Montenegro). This state aspired to the status of sole legal successor to the SFRY, but those claims were opposed by the other former republics. Eventually, it accepted the opinion of the Badinter Arbitration Committee about shared succession[10] and in 2003 its official name was changed to Serbia and Montenegro. This state dissolved when Montenegro and Serbia each became independent states in 2006, with Kosovo having an ongoing dispute over its declaration of independence in 2008.
- ^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia, 1955" (PDF). publikacije.stat.gov.rs. Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia Federal Statistical Office.
- ^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia, 1965" (PDF). publikacije.stat.gov.rs. Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia Federal Statistical Office.
- ^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia, 1975" (PDF). publikacije.stat.gov.rs. Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia Federal Statistical Office.
- ^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia, 1985" (PDF). publikacije.stat.gov.rs. Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia Federal Statistical Office.
- ^ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia, 1991" (PDF). publikacije.stat.gov.rs. Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia Federal Statistical Office.
- ^ Spencer Tucker. Encyclopedia of World War I: A Political, Social, and Military History. Santa Barbara, California, US: ABC-CLIO, 2005. Pp. 1189.
- ^ "orderofdanilo.org". Archived from the original on 16 May 2009.
- ^ Huntington, Samuel P. (1996). The clash of civilizations and the remaking of world order. Simon & Schuster. p. 260. ISBN 978-0-684-84441-1.
- ^ "History, bloody history". BBC News. 24 March 1999. Archived from the original on 25 January 2009. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- ^ "FR Yugoslavia Investment Profile 2001" (PDF). EBRD Country Promotion Programme. p. 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 September 2011.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).