
Back Arteria AN شريان Arabic ܫܪܝܢܐ ARC Arteria AST Arteriyalar Azerbaijani Артерия Bashkir Артэрыя Byelorussian Артерия Bulgarian ধমনি Bengali/Bangla Arterija BS
| Artery | |
|---|---|
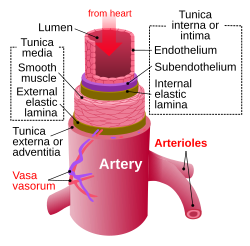 Diagram of an artery | |
| Details | |
| System | Circulatory system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria (plural: arteriae) |
| Greek | ἀρτηρία |
| MeSH | D001158 |
| TA98 | A12.0.00.003 |
| TA2 | 3896 |
| FMA | 50720 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
An artery (from Greek ἀρτηρία (artēríā))[1] is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in the pulmonary circulation that carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the umbilical arteries in the fetal circulation that carry deoxygenated blood to the placenta. It consists of a multi-layered artery wall wrapped into a tube-shaped channel.
Arteries contrast with veins, which carry deoxygenated blood back towards the heart; or in the pulmonary and fetal circulations carry oxygenated blood to the lungs and fetus respectively.