
Back Aspirien Afrikaans Acetylsalicylsäure ALS أسبرين Arabic Aspirina AST Asetilsalisilli turşu Azerbaijani آسپیرین AZB Eksperins BAT-SMG Aspirin BCL Ацэтылсаліцылавая кіслата Byelorussian Ацетилсалицилова киселина Bulgarian
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /əˌsiːtəlˌsælɪˈsɪlɪk/ |
| Trade names | Bayer Aspirin, others |
| Other names |
|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682878 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, rectal |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80–100%[6] |
| Protein binding | 80–90%[7] |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2C19 and possibly CYP3A), some is also hydrolysed to salicylate in the gut wall.[7] |
| Elimination half-life | Dose-dependent; 2–3 h for low doses (100 mg or less), 15–30 h for larger doses.[7] |
| Excretion | Urine (80–100%), sweat, saliva, feces[6] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.059 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
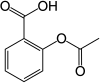
| Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molar mass | 180.159 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.40 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 135 °C (275 °F) [9] |
| Boiling point | 140 °C (284 °F) (decomposes) |
| Solubility in water | 3 g/L |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Aspirin is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic.[10] Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever.[10]
Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks, ischaemic strokes, and blood clots in people at high risk.[10] For pain or fever, effects typically begin within 30 minutes.[10] Aspirin works similarly to other NSAIDs but also suppresses the normal functioning of platelets.[10]
One common adverse effect is an upset stomach.[10] More significant side effects include stomach ulcers, stomach bleeding, and worsening asthma.[10] Bleeding risk is greater among those who are older, drink alcohol, take other NSAIDs, or are on other blood thinners.[10] Aspirin is not recommended in the last part of pregnancy.[10] It is not generally recommended in children with infections because of the risk of Reye syndrome.[10] High doses may result in ringing in the ears.[10]
A precursor to aspirin found in the bark of the willow tree (genus Salix) has been used for its health effects for at least 2,400 years.[11][12] In 1853, chemist Charles Frédéric Gerhardt treated the medicine sodium salicylate with acetyl chloride to produce acetylsalicylic acid for the first time.[13] Over the next 50 years, other chemists, mostly of the German company Bayer, established the chemical structure and devised more efficient production methods.[13]: 69–75 Felix Hoffmann (or Arthur Eichengrün) of Bayer was the first to produce acetylsalicylic acid in a pure, stable form in 1897.[14] By 1899, Bayer had dubbed this drug Aspirin and was selling it globally.[15]: 27
Aspirin is available without medical prescription as a proprietary or generic medication[10] in most jurisdictions. It is one of the most widely used medications globally, with an estimated 40,000 tonnes (44,000 tons) (50 to 120 billion pills) consumed each year,[11][16] and is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[17] In 2022, it was the 36th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 16 million prescriptions.[18][19]
- ^ McTavish J (Fall 1987). "What's in a Name? Aspirin and the American Medical Association". Bulletin of the History of Medicine. 61 (3): 343–366. JSTOR 44442097. PMID 3311247.
- ^ "Aspirin Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 2 April 2018. Retrieved 29 December 2019.
- ^ "OTC medicine monograph: Aspirin tablets for oral use". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 4 April 2023.
- ^ "Poisons Standard October 2022". Australian Government Federal Register of Legislation. 26 September 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ "Aspirin Product information". Health Canada. 22 October 2009. Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Zorprin, Bayer Buffered Aspirin (aspirin) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 3 April 2014.
- ^ a b c Brayfield A, ed. (14 January 2014). "Aspirin". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 3 April 2014.
- ^ CID 2244 from PubChem
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
b92was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Aspirin". American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. 29 November 2021. Archived from the original on 25 April 2017 – via Drugs.com.
- ^ a b Jones A (2015). Chemistry: An Introduction for Medical and Health Sciences. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 5–6. ISBN 978-0-470-09290-3.
- ^ Ravina E (2011). The Evolution of Drug Discovery: From Traditional Medicines to Modern Drugs. John Wiley & Sons. p. 24. ISBN 978-3-527-32669-3.
- ^ a b Jeffreys D (2008). Aspirin the remarkable story of a wonder drug. Bloomsbury Publishing USA. ISBN 978-1-59691-816-0. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.: 46–48
- ^ "Felix Hoffmann". Science History Institute. Retrieved 3 October 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
MannPlummer1991was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Warner TD, Mitchell JA (October 2002). "Cyclooxygenase-3 (COX-3): filling in the gaps toward a COX continuum?". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (21): 13371–3. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9913371W. doi:10.1073/pnas.222543099. PMC 129677. PMID 12374850.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Aspirin Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.