
Back Bilirubien Afrikaans بيليروبين Arabic بيليروبين ARY بیلیروبین AZB Білірубін Byelorussian Билирубин Bulgarian বিলিরুবিন Bengali/Bangla Bilirubin BS Bilirubina Catalan بیلیڕووبین CKB
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
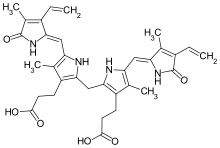
3,3′-(2,17-Diethenyl-3,7,13,18-tetramethyl-1,19-dioxo-10,19,21,22,23,24-hexahydro-1H-biline-8,12-diyl)dipropanoic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3,3′-([12(2)Z,6(72)Z]-13,74-Diethenyl-14,33,54,73-tetramethyl-15,75-dioxo-11,15,71,75-tetrahydro-31H,51H-1,7(2),3,5(2,5)-tetrapyrrolaheptaphane-12(2),6(72)-diene-34,53-diyl)dipropanoic acid | |
| Other names
Bilirubin IXα
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.218 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C33H36N4O6 | |
| Molar mass | 584.673 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.31 g·cm-3[1] |
| Melting point | 235°C[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Bilirubin (BR) (adopted from German, originally bili—bile—plus ruber—red—from Latin) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normcomponent of the straw-yellow color in urine.[3] Another breakdown product, stercobilin, causes the brown color of feces.
Although bilirubin is usually found in animals rather than plants, at least one plant species, Strelitzia nicolai, is known to contain the pigment.[4]
- ^ Bonnett, Raymond; Davies, John E.; Hursthouse, Michael B. (July 1976). "Structure of bilirubin". Nature. 262 (5566): 326–328. Bibcode:1976Natur.262..326B. doi:10.1038/262326a0. PMID 958385. S2CID 4278361.
- ^ Sturrock, E. D.; Bull, J. R.; Kirsch, R. E. (March 1994). "The synthesis of [10-13C]bilirubin IXα". Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals. 34 (3): 263–274. doi:10.1002/jlcr.2580340309.
- ^ Chew, Dennis J.; DiBartola, Stephen P.; Schenck, Patricia A. (1 January 2011), Chew, Dennis J.; DiBartola, Stephen P.; Schenck, Patricia A. (eds.), "Chapter 1 - Urinalysis", Canine and Feline Nephrology and Urology (Second Edition), Saint Louis: W.B. Saunders, pp. 1–31, ISBN 978-0-7216-8178-8, retrieved 1 November 2023
- ^ Pirone C, Quirke JM, Priestap HA, Lee DW (March 2009). "Animal pigment bilirubin discovered in plants". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 131 (8): 2830. doi:10.1021/ja809065g. PMC 2880647. PMID 19206232.