
Back Rat für gegenseitige Wirtschaftshilfe ALS مجلس التعاون الاقتصادي Arabic COMECON AST Qarşılıqlı İqtisadi Yardım Şurası Azerbaijani Үҙ-ара иҡтисади ярҙам советы Bashkir Савет эканамічнай узаемадапамогі Byelorussian Съвет за икономическа взаимопомощ Bulgarian Consell d'Assistència Econòmica Mútua Catalan Rada vzájemné hospodářské pomoci Czech Comecon Danish
Council for Mutual Economic Assistance Совет Экономической Взаимопомощи | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1949–1991 | |||||||
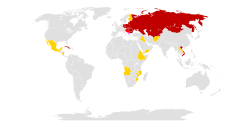 Map of Comecon member states as of November 1986 Comecon as of November 1986: Members Members that left the Warsaw Pact (Albania) Associate members Observers | |||||||
| Headquarters | Moscow, Soviet Union | ||||||
| Official languages | |||||||
| Type | Economic union | ||||||
| Member states | |||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||
• Organization established | 25 January 1949 | ||||||
• Dissolution of Comecon | 28 June 1991 | ||||||
| 25 December 1991 | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
| 1960 | 23,422,281 km2 (9,043,393 sq mi) | ||||||
| 1989 | 25,400,231 km2 (9,807,084 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 1989 | 504 million | ||||||
| Currency | |||||||
| |||||||
| Eastern Bloc |
|---|
 |
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance,[c] often abbreviated as Comecon (/ˌkɒmɪˈkɒn/ KOM-ik-ON), was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc along with a number of socialist states elsewhere in the world.[1]
The descriptive term was often applied to all multilateral activities involving members of the organization, rather than being restricted to the direct functions of Comecon and its organs.[2] This usage was sometimes extended as well to bilateral relations among members because in the system of communist international economic relations, multilateral accords – typically of a general nature – tended to be implemented through a set of more detailed, bilateral agreements.[3]
Comecon was the Eastern Bloc's response to the formation in Western Europe of the Marshall Plan and the OEEC, which later became the OECD.[3]
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Michael C. Kaser, Comecon: Integration problems of the planned economies (Oxford University Press, 1967).
- ^ For example, this is the usage in the Library of Congress Country Study that is heavily cited in the present article.
- ^ a b "Appendix B: The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance: Germany (East)". Library of Congress Country Study. Archived from the original on 1 May 2009.

