
Back دودة حاسوب Arabic Kompüter soxulcanı Azerbaijani Сеткавы чарвяк Byelorussian Компютърен червей Bulgarian कंप्यूटर वर्म Bihari কম্পিউটার ওয়ার্ম Bengali/Bangla Računarski crv BS Cuc (informàtica) Catalan کرمی کۆمپیوتەر CKB Počítačový červ Czech
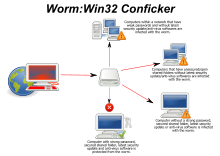
A computer worm is a standalone malware computer program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers.[1] It often uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security failures on the target computer to access it. It will use this machine as a host to scan and infect other computers. When these new worm-invaded computers are controlled, the worm will continue to scan and infect other computers using these computers as hosts, and this behaviour will continue.[2] Computer worms use recursive methods to copy themselves without host programs and distribute themselves based on exploiting the advantages of exponential growth, thus controlling and infecting more and more computers in a short time.[3] Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the network, even if only by consuming bandwidth, whereas viruses almost always corrupt or modify files on a targeted computer.
Many worms are designed only to spread, and do not attempt to change the systems they pass through. However, as the Morris worm and Mydoom showed, even these "payload-free" worms can cause major disruption by increasing network traffic and other unintended effects.
- ^ Barwise, Mike. "What is an internet worm?". BBC. Archived from the original on 2015-03-24. Retrieved 9 September 2010.
- ^ Zhang, Changwang; Zhou, Shi; Chain, Benjamin M. (2015-05-15). "Hybrid Epidemics—A Case Study on Computer Worm Conficker". PLOS ONE. 10 (5): e0127478. arXiv:1406.6046. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1027478Z. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0127478. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4433115. PMID 25978309.
- ^ Marion, Jean-Yves (2012-07-28). "From Turing machines to computer viruses". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 370 (1971): 3319–3339. Bibcode:2012RSPTA.370.3319M. doi:10.1098/rsta.2011.0332. ISSN 1364-503X. PMID 22711861.