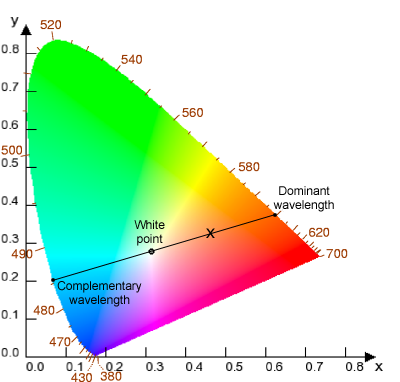
The "x" marks the color in question. For the white point indicated, the dominant wavelength for "x" is on the nearer perimeter, around 600 nm, while the complementary wavelength is opposite, around 485 nm. Intuitively, the dominant wavelength of "x" corresponds to the primary hue of "x".
In color science, the dominant wavelength is a method of approximating a color's hue. Along with purity, it makes up one half of the Helmholtz coordinates. The dominant wavelength of a given color is defined to be the wavelength of monochromatic spectral light that lies on the straight line passing through the white point and the given colour in the chromaticity diagram.[1]
- ^ Schanda, Janos (2007). Colorimetry : understanding the CIE system. [Vienna, Austria]: CIE/Commission internationale de l'eclairage. pp. 65–66. ISBN 978-0-470-04904-4.
