
Back Endocrinolochía AN علم الغدد الصم Arabic Endokrinologiya Azerbaijani Эндокринология Bashkir Эндакрыналогія Byelorussian Ендокринология Bulgarian অন্তঃক্ষরা গ্রন্থিবিজ্ঞান Bengali/Bangla Endokrinologija BS Endocrinologia Catalan Endokrinologie Czech
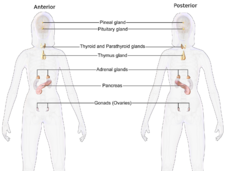 Illustration depicting the primary endocrine organs of a female | |
| System | Endocrine |
|---|---|
| Significant diseases | Diabetes, Thyroid disease, Androgen excess |
| Significant tests | Thyroid function tests, Blood sugar levels |
| Specialist | Endocrinologist |
| Glossary | Glossary of medicine |
Endocrinology (from endocrine + -ology) is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events proliferation, growth, and differentiation, and the psychological or behavioral activities of metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sleep, digestion, respiration, excretion, mood, stress, lactation, movement, reproduction, and sensory perception caused by hormones. Specializations include behavioral endocrinology and comparative endocrinology.[1]
The endocrine system consists of several glands, all in different parts of the body, that secrete hormones directly into the blood rather than into a duct system. Therefore, endocrine glands are regarded as ductless glands. Hormones have many different functions and modes of action; one hormone may have several effects on different target organs, and, conversely, one target organ may be affected by more than one hormone.
- ^ Al-hussaniy, Hany; AL-Biati, Haedar A (2022-10-12). "The Role of Leptin Hormone, Neuropeptide Y, Ghrelin and Leptin/Ghrelin ratio in Obesogenesis". Medical and Pharmaceutical Journal. 1 (2): 12–23. doi:10.55940/medphar20227. ISSN 2957-6067.