Back غرينادين Arabic Грэнадзіны Byelorussian Grenadinez Breton Grenadines Catalan Grenadines (kapuloan) CEB Grenadiny Czech Grenadinen German Γρεναδίνες Greek Grenadinoj Esperanto Granadinas Spanish
 | |||||||||||||
| Geography | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Caribbean | ||||||||||||
| Archipelago | Lesser Antilles | ||||||||||||
| Total islands | 32 | ||||||||||||
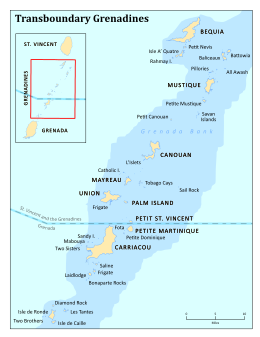
| Major islands | Carriacou, Young Island, Bequia, Mustique, Canouan, Union Island, Mayreau, Petit St Vincent, and Palm Island. | ||||||||||||
| Area | 86 km2 (33 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Administration | |||||||||||||
| Demographics | |||||||||||||
| Demonym | Grenadinese | ||||||||||||
| Additional information | |||||||||||||
| Time zone | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
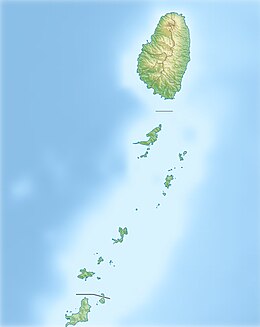
The Grenadines (/ˈɡrɛnədiːnz/) is a chain of small islands that lie on a line between the larger islands of Saint Vincent and Grenada in the Lesser Antilles. Nine are inhabited and open to the public (or ten, if the offshore island of Young Island is counted): Bequia, Mustique, Canouan, Union Island, Petit St Vincent, Palm Island and Mayreau, all in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, plus Petite Martinique and Carriacou in Grenada. Several additional privately owned islands, such as Calivigny, are also inhabited. Notable uninhabited islands of the Grenadines include Petit Nevis, used by whalers, and Petit Mustique, which was the centre of a prominent real estate scam in the early 2000s.
The northern two-thirds of the chain, including about 32 islands and cays, is part of the country of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. The southern third of the chain belongs to the country of Grenada. Carriacou is the largest and most populous of the Grenadines.