Back Heksaan Afrikaans هكسان Arabic Heksan Azerbaijani هقزان AZB Гексан Byelorussian Хексан Bulgarian হেক্সেন Bengali/Bangla Heksan BS Hexà Catalan Hexan Czech
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexane[2] | |||
| Other names
Sextane,[1] hexacarbane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1730733 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.435 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 1985 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | n-hexane | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1208 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H14 | |||
| Molar mass | 86.178 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Petrolic | ||
| Density | 0.6606 g mL−1[3] | ||
| Melting point | −96 to −94 °C; −141 to −137 °F; 177 to 179 K | ||
| Boiling point | 68.5 to 69.1 °C; 155.2 to 156.3 °F; 341.6 to 342.2 K | ||
| 9.5 mg L−1 | |||
| log P | 3.764 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 17.60 kPa (at 20.0 °C) | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
7.6 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 | ||
| UV-vis (λmax) | 200 nm | ||
| −74.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.375 | ||
| Viscosity | 0.3 mPa·s | ||
| 0.08 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
265.2 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
296.06 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−199.4–−198.0 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−4180–−4140 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Reproductive toxicity – After aspiration, pulmonary oedema, pneumonitis[4] | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H302, H305, H315, H336, H361fd, H373, H411 | |||
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P235, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P271, P273, P280, P281, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P308+P313, P310, P312, P314, P332+P313, P363, P370+P378, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −26.0 °C (−14.8 °F; 247.2 K) | ||
| 234.0 °C (453.2 °F; 507.1 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.2–7.7% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
25 g kg−1 (oral, rat) 28710 mg/kg (rat, oral)[6] | ||
LDLo (lowest published)
|
56137 mg/kg (rat, oral)[6] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 500 ppm (1800 mg/m3)[5] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 50 ppm (180 mg/m3)[5] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1100 ppm[5] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanes
|
|||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Hexane (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
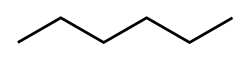
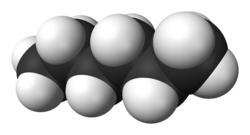
Hexane (/ˈhɛkseɪn/) or n-hexane is an organic compound, a straight-chain alkane with six carbon atoms and the molecular formula C6H14.[7]
Hexane is a colorless liquid, odorless when pure, and with a boiling point of approximately 69 °C (156 °F). It is widely used as a cheap, relatively safe, largely unreactive, and easily evaporated non-polar solvent, and modern gasoline blends contain about 3% hexane.[8]
The term hexanes refers to a mixture, composed largely (>60%) of n-hexane, with varying amounts of the isomeric compounds 2-methylpentane and 3-methylpentane, and possibly, smaller amounts of nonisomeric C5, C6, and C7 (cyclo)alkanes. These "hexanes" mixtures are cheaper than pure hexane and are often used in large-scale operations not requiring a single isomer (e.g., as cleaning solvent or for chromatography).
- ^ Hofmann, August Wilhelm Von (1 January 1867). "I. On the action of trichloride of phosphorus on the salts of the aromatic monamines". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. 15: 54–62. doi:10.1098/rspl.1866.0018. S2CID 98496840.
- ^ "n-hexane – Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Archived from the original on 8 March 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- ^ William M. Haynes (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. pp. 3–298. ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3.
- ^ GHS Classification on [PubChem]
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0322". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b "n-Hexane". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ PubChem. "n-HEXANE". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 3 November 2023.
- ^ "n-Hexane - Hazardous Agents". Haz-Map. Retrieved 7 July 2022.