
Back Himalaja Afrikaans Himalaya ALS ሂማላያ ተራሮች Amharic Himalaya AN हिमालय ANP هملايا Arabic هيمالايا ARZ হিমালয় Assamese Himalaya AST Гьималаял AV
| The Himalayas | |
|---|---|
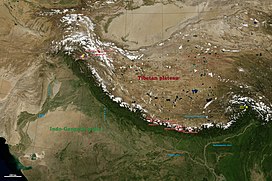 The arc of the Himalayas (also Hindu Kush and Karakorams) showing the eight-thousanders (in red); Indo-Gangetic Plain; Tibetan plateau; rivers Indus, Ganges, and Yarlung Tsangpo-Brahmaputra; and the two anchors of the range (in yellow) | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Mount Everest, Nepal, China |
| Elevation | 8,848.86 m (29,031.7 ft) |
| Coordinates | 27°59′N 86°55′E / 27.983°N 86.917°E |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 2,400 km (1,500 mi) |
| Geography | |
 Mount Everest and surrounding peaks as seen from the north-northwest over the Tibetan Plateau. Four eight-thousanders can be seen, Makalu (8,462 m), Everest (8,848 m), Cho Oyu (8,201 m), and Lhotse (8,516 m). | |
| Countries | [a] |
| Continent | Asia |
| Geology | |
| Orogeny | Alpine orogeny |
| Rock age | Cretaceous to Cenozoic |
| Rock types | |
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (/ˌhɪməˈleɪ.ə, hɪˈmɑːləjə/ HIM-ə-LAY-ə, hih-MAH-lə-yə)[b] is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than 100 peaks exceeding elevations of 7,200 m (23,600 ft) above sea level lie in the Himalayas.
The Himalayas abut on or cross territories of six countries: Nepal, China, Pakistan, Bhutan, India and Afghanistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China.[4] The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus, the Ganges, and the Tsangpo–Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their combined drainage basin is home to some 600 million people; 53 million people live in the Himalayas.[5] The Himalayas have profoundly shaped the cultures of South Asia and Tibet. Many Himalayan peaks are sacred in Hinduism and Buddhism. The summits of several—Kangchenjunga (from the Indian side), Gangkhar Puensum, Machapuchare, Nanda Devi, and Kailash in the Tibetan Transhimalaya—are off-limits to climbers.
The Himalayas were uplifted after the collision of the Indian tectonic plate with the Eurasian plate, specifically, by the folding, or nappe-formation of the uppermost Indian crust, even as a lower layer continued to push on into Tibet and add thickness to its plateau; the still lower crust, along with the mantle, however, subducted under Eurasia. The Himalayan mountain range runs west-northwest to east-southeast in an arc 2,400 km (1,500 mi) long.[6] Its western anchor, Nanga Parbat, lies just south of the northernmost bend of the Indus river. Its eastern anchor, Namcha Barwa, lies immediately west of the great bend of the Yarlung Tsangpo River. The Indus-Yarlung suture zone, along which the headwaters of these two rivers flow, separates the Himalayas from the Tibetan plateau; the rivers also separate the Himalayas from the Karakorams, the Hindu Kush, and the Transhimalaya. The range varies in width from 350 km (220 mi) in the west to 150 km (93 mi) in the east.[7]
- ^ Himalayas (mountains, Asia). Encyclopaedia Britannica. 14 August 2023.
Though India, Nepal, and Bhutan have sovereignty over most of the Himalayas, Pakistan and China also occupy parts of them. In the Kashmir region, Pakistan has administrative control of some 32,400 square miles (83,900 square km) of the range lying north and west of the "line of control" established between India and Pakistan in 1972. China administers some 14,000 square miles (36,000 square km) in the Ladakh region and has claimed territory at the eastern end of the Himalayas within the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. Those disputes accentuate the boundary problems faced by India and its neighbours in the Himalayan region.
- ^ Zurick, David; Pocheco, Julsun (2006), Illustrated Atlas of the Himalaya, University Press of Kentucky, p. 8,11,12, ISBN 9780813173849
- ^ "Himalayan". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
Etymology: < Himālaya (Sanskrit < hima snow + ālaya dwelling, abode) + -an suffix)
(Subscription or participating institution membership required.) - ^ Bishop, Barry. "Himalayas (mountains, Asia)". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 30 July 2016.
- ^ A.P. Dimri; B. Bookhagen; M. Stoffel; T. Yasunari (8 November 2019). Himalayan Weather and Climate and their Impact on the Environment. Springer Nature. p. 380. ISBN 978-3-030-29684-1.
- ^ Wadia, D. N. (1931). "The syntaxis of the northwest Himalaya: its rocks, tectonics and orogeny". Record Geol. Survey of India. 65 (2): 189–220.
- ^ Apollo, M. (2017). "Chapter 9: The population of Himalayan regions – by the numbers: Past, present and future". In Efe, R.; Öztürk, M. (eds.). Contemporary Studies in Environment and Tourism. Cambridge Scholars Publishing. pp. 143–159.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).