
Back تاريخ القياس Arabic পরিমাপের ইতিহাস Bengali/Bangla Geschichte der Maße und Gewichte German Histoire de la mesure French היסטוריה של שיטות המדידה HE मापन का इतिहास Hindi Байырғы қазақ өлшемдері Kazakh Древние единицы измерения Russian Zgodovina merjenja Slovenian Vipimo asilia vya Kiswahili Swahili
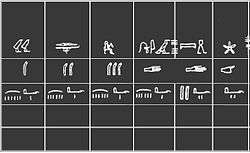
The earliest recorded systems of weights and measures originate in the 3rd or 4th millennium BC.[1] Even the very earliest civilizations needed measurement for purposes of agriculture, construction and trade. Early standard units might only have applied to a single community or small region, with every area developing its own standards for lengths, areas, volumes and masses. Often such systems were closely tied to one field of use, so that volume measures used, for example, for dry grains were unrelated to those for liquids, with neither bearing any particular relationship to units of length used for measuring cloth or land. With development of manufacturing technologies, and the growing importance of trade between communities and ultimately across the Earth, standardized weights and measures became critical. Starting in the 18th century, modernized, simplified and uniform systems of weights and measures were developed, with the fundamental units defined by ever more precise methods in the science of metrology. The discovery and application of electricity was one factor motivating the development of standardized internationally applicable units.
- ^ "A Brief History of Metrology - bowersUK". bowers rest of world. Retrieved October 10, 2024.