
Back কাদাম্বা লিপি Assamese Alfabeto kadamba Spanish कदंब लिपि Hindi ಕದಂಬ ಲಿಪಿ Kannada കദംബ ലിപി Malayalam ਕਦੰਬਾ ਲਿਪੀ Punjabi Pismo kadamba Polish Escrita kadamba Portuguese Кадамба (письмо) Russian อักษรกทัมพะ Thai
| Kadamba script | |
|---|---|
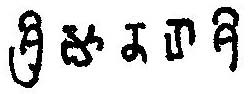 | |
| Script type | |
Period | 4–7th century CE[1] |
| Direction | Left-to-right |
| Languages | Kannada Telugu Sanskrit Konkani |
| Related scripts | |
Parent systems | |
Child systems | Kannada-Telugu alphabet, Goykanadi,[2] Pyu script[3] |
| Brahmic scripts |
|---|
| The Brahmi script and its descendants |
The Kadamba script is the first writing system devised specifically for writing Kannada, and it was later adopted to write the Telugu language.[4] The Kadamba script is also known as Pre-Old-Kannada script.
The Kadamba script is one of the oldest scripts of the southern group of writing systems that developed from the ancient Brahmi script. By the 5th century CE it became distinct from other Brahmi variants and was used in what are now the South Indian states of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. It evolved into the Kannada-Telugu script by the 10th century CE and was used to write the Kannada and Telugu languages.[5] It is also distantly related to the Sinhala script.[6]
- ^ Diringer, David (1948). Alphabet a key to the history of mankind. p. 381.
- ^ "Goykanadi script".
- ^ Aung-Thwin, Michael (2005). The mists of Rāmañña: The Legend that was Lower Burma (illustrated ed.). Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-2886-8.
- ^ Diringer, David (1948). Alphabet a key to the history of mankind. p. 381.
- ^ "Scripts fading away with time". Retrieved 28 August 2013.
- ^ Jayarajan, Paul M. (1 January 1976). History of the Evolution of the Sinhala Alphabet. Colombo Apothecaries' Company, Limited.