| Lake Chippewa | |
|---|---|
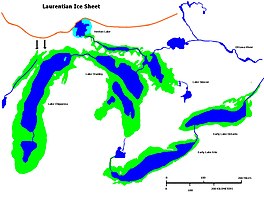 Glacial Lakes Chippewa, Stanley, Early Erie and Early Ontario. Low level lake stages during the end of the Wisconsin Glacial era in North America. Based on Larsen map, 1987. | |
| Location | North America |
| Group | Great Lakes |
| Coordinates | 44°N 87°W / 44°N 87°W |
| Lake type | former lake |
| Etymology | Chippewa People |
| Primary inflows | Laurentide Ice Sheet |
| Primary outflows | Grand River valley in Michigan |
| Basin countries | Canada United States |
| First flooded | 9,500 years before present |
| Max. length | 220 mi (350 km) |
| Max. width | 30 mi (48 km) |
| Residence time | 7300 years in existence |
| Surface elevation | 230 ft (70 m)[1] |
| References | United States Geological Survey, George Otis Smith, Director; The Pleistocene of Indiana and Michigan and the History of the Great Lakes; Frank Leverett and Frank B. Taylor; Department of the Interior, Monographs of the United States Geological Survey; Volume LIII; Washington; Government Printing Office; 1915 |
Lake Chippewa was a prehistoric proglacial lake. The basin is now Lake Michigan. It formed about 10,600 years before present (YBP). The lake occupied the depression left by the Michigan Lobe of the Laurentide Ice Sheet.[2]
- ^ Glacial Lakes Chippewa and Stanley (Map). Randall Schaetzl, Michigan State University. Retrieved January 27, 2020.
- ^ University of Wisconsin, Green Bay, Dept of Geology[full citation needed]

