
Back Caixa i metxa Catalan Tapsamling Danish Zapfenverbindung German Σύνδεσμος μόρσου - εγκοπής Greek Mortezo kaj tenono Esperanto Caja y espiga Spanish Tapp (tisleritöö) Estonian Aho-zirika Basque مورتیس و تنون Persian Mortaise (menuiserie) French
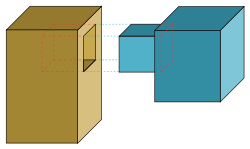


A mortise and tenon (occasionally mortice and tenon) is a joint that connects two pieces of wood or other material. Woodworkers around the world have used it for thousands of years to join pieces of wood, mainly when the adjoining pieces connect at right angles, though it can be used to connect two work pieces at any angle.
Mortise-and tenon-joints are simple, strong, and stable, and can be used in many projects and which give an attractive look. They are either glued or friction-fitted into place. This joint is difficult to make, because of the precise measuring and tight cutting required; as such, modern woodworkers often use machinery specifically designed to cut mortises and matching tenons quickly and easily. Still, many woodworkers cut them by hand in a traditional manner. There are many variations of this type of joint, but its basic structure has two components, the mortise hole and the tenon tongue.
The tenon, formed on the end of a member generally referred to as a rail, fits into a square or rectangular hole cut into the other, corresponding member. The tenon is cut to fit the mortise hole exactly. It usually has shoulders that seat when the joint fully enters the mortise hole. The joint may be glued, pinned, or wedged to lock it in place.
This joint is also used with other materials, as traditionally by both stonemasons and blacksmiths.