
Back OS ACE Bedryfstelsel (inligtingstegnologie) Afrikaans Betriebssystem ALS የሲስተም አሰሪ Amharic Sistema operativo AN Weorcendebyrdness ANG نظام تشغيل Arabic نظام تشغيل ARZ Sistema operativu AST Əməliyyat sistemi Azerbaijani
| Operating systems |
|---|
 |
| Common features |
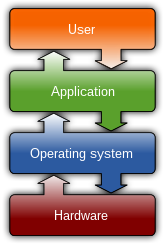
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, peripherals, and other resources.
For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware,[1][2] although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer – from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers.
As of September 2024[update], Android is the most popular operating system with a 46% market share, followed by Microsoft Windows at 26%, iOS and iPadOS at 18%, macOS at 5%, and Linux at 1%. Android, iOS, and iPadOS are mobile operating systems, while Windows, macOS, and Linux are desktop operating systems.[3] Linux distributions are dominant in the server and supercomputing sectors. Other specialized classes of operating systems (special-purpose operating systems),[4][5] such as embedded and real-time systems, exist for many applications. Security-focused operating systems also exist. Some operating systems have low system requirements (e.g. light-weight Linux distribution). Others may have higher system requirements.
Some operating systems require installation or may come pre-installed with purchased computers (OEM-installation), whereas others may run directly from media (i.e. live CD) or flash memory (i.e. USB stick).
- ^ Stallings (2005). Operating Systems, Internals and Design Principles. Pearson: Prentice Hall. p. 6.
- ^ Dhotre, I.A. (2009). Operating Systems. Technical Publications. p. 1.
- ^ "Operating System Market Share Worldwide". StatCounter Global Stats. Retrieved 20 December 2024.
- ^ "VII. Special-Purpose Systems - Operating System Concepts, Seventh Edition [Book]". www.oreilly.com. Archived from the original on 13 June 2021. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- ^ "Special-Purpose Operating Systems - RWTH AACHEN UNIVERSITY Institute for Automation of Complex Power Systems - English". www.acs.eonerc.rwth-aachen.de. Archived from the original on 14 June 2021. Retrieved 8 February 2021.