
Back لوزة حنكية Arabic Hueg Breton Amígdala palatina Catalan Krční mandle Czech Tonsilla palatina German ތަލީގެ ޓޮންސިލް DV Amígdala palatina Spanish لوزههای کامی Persian Nielurisa Finnish Tonsille palatine French
| Palatine tonsil | |
|---|---|
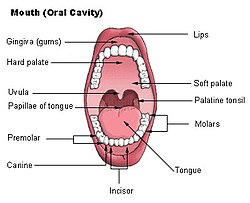 Mouth (oral cavity) | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Pharyngeal pouches |
| System | Immune system (lymphatic system) |
| Artery | Tonsillar branch of the facial artery |
| Nerve | Tonsillary branches of lesser palatine nerves |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tonsilla palatina |
| MeSH | D014066 |
| TA98 | A05.2.01.011 |
| TA2 | 2853, 5181 |
| FMA | 9610 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Palatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils,[1] are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat in humans and other mammals, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish lumps. Tonsils only present as "white lumps" if they are inflamed or infected with symptoms of exudates (pus drainage) and severe swelling.
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils and will often, but not necessarily, cause a sore throat and fever.[2] In chronic cases, tonsillectomy may be indicated.[3]
- ^ Merati AL, Rieder AA (August 2003). "Normal endoscopic anatomy of the pharynx and larynx". Am. J. Med. 115 Suppl 3A (3): 10S – 14S. doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(03)00187-6. PMID 12928069.
- ^ Georgalas, Christos C.; Tolley, Neil S.; Narula, Professor Anthony (2014-07-22). "Tonsillitis". BMJ Clinical Evidence. 2014: 0503. ISSN 1752-8526. PMC 4106232. PMID 25051184.
- ^ Weil-Olivier C, Sterkers G, François M, Garnier J, Reinert P, Cohen R (2006). "[Tonsillectomy in 2005]". Arch Pediatr. 13 (2): 168–74. doi:10.1016/j.arcped.2005.10.016. PMID 16386410.