Back بوابة:التشيك Arabic Portal:Çexiya Azerbaijani Портал:Чехия Bulgarian Portál:Česko Czech Portal:Tschechien German Portalo:Ĉeĥio Esperanto Portal:República Checa Spanish Portail:Tchéquie French Portál:Csehország Hungarian Portale:Repubblica Ceca Italian
Welcome to the Czech Portal!
Vítejte na Českém portálu!

|

|

| |
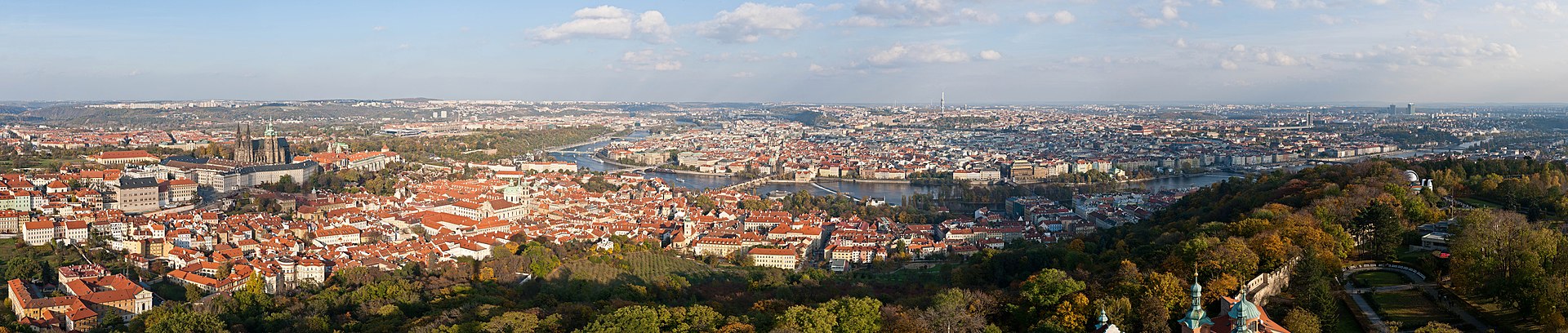
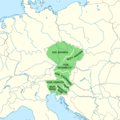
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The Czech Republic has a hilly landscape that covers an area of 78,871 square kilometers (30,452 sq mi) with a mostly temperate continental and oceanic climate. The capital and largest city is Prague; other major cities and urban areas include Brno, Ostrava, Plzeň and Liberec.
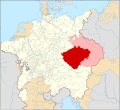
The Duchy of Bohemia was founded in the late 9th century under Great Moravia. It was formally recognized as an Imperial Estate of the Holy Roman Empire in 1002 and became a kingdom in 1198. Following the Battle of Mohács in 1526, all of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown were gradually integrated into the Habsburg monarchy. Nearly a hundred years later, the Protestant Bohemian Revolt led to the Thirty Years' War. After the Battle of White Mountain, the Habsburgs consolidated their rule. With the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the Crown lands became part of the Austrian Empire.
In the 19th century, the Czech lands became more industrialized; further, in 1918, most of the country became part of the First Czechoslovak Republic following the collapse of Austria-Hungary after World War I. Czechoslovakia was the only country in Central and Eastern Europe to remain a parliamentary democracy during the entirety of the interwar period. After the Munich Agreement in 1938, Nazi Germany systematically took control over the Czech lands. Czechoslovakia was restored in 1945 and three years later became an Eastern Bloc communist state following a coup d'état in 1948. Attempts to liberalize the government and economy were suppressed by a Soviet-led invasion of the country during the Prague Spring in 1968. In November 1989, the Velvet Revolution ended communist rule in the country and restored democracy. On 31 December 1992, Czechoslovakia was peacefully dissolved, with its constituent states becoming the independent states of the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
The Czech Republic is a unitary parliamentary republic and developed country with an advanced, high-income social market economy. It is a welfare state with a European social model, universal health care and free-tuition university education. It ranks 32nd in the Human Development Index. The Czech Republic is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the European Union, the OECD, the OSCE, the Council of Europe and the Visegrád Group. (Full article...)
Selected article -
Sněžka (Czech pronunciation: [ˈsɲɛʃka] ⓘ) or Śnieżka (Polish pronunciation: [ˈɕɲɛʂka], German: Schneekoppe, Slovak: Snežka) is a mountain on the border between the Czech Republic and Poland, the most prominent point of the Silesian Ridge in the Giant Mountains. At 1,603.3 metres (5,260 ft), its summit is the highest point in the Czech Republic, in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in the Giant Mountains and in the entire Sudetes. (Full article...)
Selected picture

Source: Národní Galerie v Praze, PD
In this month
- 2 March 1978 – Vladimír Remek becomes the first man in space from a country other than the United States and USSR
- 6 March 1645 – One of the bloodiest battles of the Thirty Years' War, the Battle of Jankau takes place 50km from Prague
- 16 March 1939 – The Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia is established following the end of the Second Czechoslovak Republic
- 29 March 1896 – The first Prague derby is played between Sparta and Slavia. The match ends 0–0
- 30 March 1968 – Ludvík Svoboda (pictured) is elected President of Czechoslovakia
Categories
Selected biography -
Pavel Nedvěd (Czech pronunciation: [ˈpavɛl ˈnɛdvjɛt] ⓘ; born 30 August 1972) is a Czech former professional footballer who played as a midfielder. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest Czech players of all time and he won numerous trophies with Italian clubs Lazio and Juventus. He won the last ever Cup Winners' Cup with Lazio and led Juventus to the 2003 UEFA Champions League final.
Nedvěd was a vital player in the Czech team that reached the final of Euro 1996 and afterwards he attracted the attention of big European clubs. He also captained the team at UEFA Euro 2004, where they were defeated in the semi-final by eventual champions Greece, and Nedvěd was named in the Team of the Tournament. Furthermore, Nedvěd helped his team qualify for the 2006 FIFA World Cup for the first time since the breakup of Czechoslovakia. Due to his quick and energetic runs during matches, Nedvěd was nicknamed "Furia Ceca" ("Czech Fury") by Italian football fans. His nickname in Czech is Méďa ("Little Bear"), stemming from the similarity between his surname and the Czech word for bear, Medvěd. (Full article...)
Did you know?
- ...that, although Mozart never visited Kroměříž, much of the Academy Award-winning film Amadeus was filmed at the local episcopal residence?
- ... that the Cross of Merit of the Minister of Defence of the Czech Republic is the highest award presented by the Czech Minister of Defence?
- ... that footballer Petr Vrabec won six Czechoslovak league titles with Sparta Prague?
- ... that Miroslav Tyrš, the founder of Czech national sport movement Sokol, was born into a German family?
General images
Related portals
Topics

Czech lands: Bohemia • Moravia • Czech Silesia
History: Únětice culture • Boii • Marcomanni • Samo • Great Moravia • Přemyslid dynasty • Lands of the Bohemian Crown • Czech lands (1526–1648) • 1648–1867 • 1867–1918) • Czechoslovakia • Czech Republic
Geography: Lakes • Protected areas • Regions • Rivers
Law: Judiciary • Law enforcement • Supreme Court of the Czech Republic
Politics: Administrative divisions • Government • Constitution • Elections • Foreign relations • Army • Parliament • Political parties • President • Prime Minister
Economy: Banks • Czech koruna • Energy • Oil and gas deposits • Stock Exchange • Tourism • Transport
Culture: Architecture • Art • Cinema • Cuisine • Demographics • Education • Language • Literature • Media • Music • Philosophy • Prostitution • Public holidays • Religion • Sport • Television • Video games
Symbols: Flag • Coat of arms • National anthem (Kde domov můj)
Lists: Outline of the Czech Republic • List of Czech Republic–related topics
WikiProjects
Featured and good content
Things to do
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus