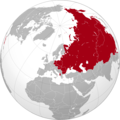
UNION OF SOVIET SOCIALIST REPUBLICS
Coat of arms of the Soviet Union 1
The flag of the Soviet Union The
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (
USSR ), commonly known as the
Soviet Union , was a
transcontinental country that spanned much of
Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. During its existence, it was the
largest country by area , extending across
eleven time zones and sharing
borders with twelve countries , and the
third-most populous country . An overall successor to the
Russian Empire , it was nominally organized as a
federal union of
national republics , the largest and most populous of which was the
Russian SFSR . In practice,
its government and
economy were
highly centralized . As a
one-party state governed by the
Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU), it was a flagship
communist state . Its capital and largest city was
Moscow .
The Soviet Union's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917. The new government, led by Vladimir Lenin , established the Russian SFSR, the world's first constitutionally socialist state . The revolution was not accepted by all within the Russian Republic , resulting in the Russian Civil War . The Russian SFSR and its subordinate republics were merged into the Soviet Union in 1922. Following Lenin's death in 1924, Joseph Stalin came to power, inaugurating rapid industrialization and forced collectivization that led to significant economic growth but contributed to a famine between 1930 and 1933 that killed millions. The Soviet forced labour camp system of the Gulag was expanded. During the late 1930s, Stalin's government conducted the Great Purge to remove opponents, resulting in mass death, imprisonment, and deportation. In 1939, the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany signed a nonaggression pact , but in 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union in the largest land invasion in history, opening the Eastern Front of World War II . The Soviets played a decisive role in defeating the Axis powers , suffering an estimated 27 million casualties , which accounted for most Allied losses. In the aftermath of the war , the Soviet Union consolidated the territory occupied by the Red Army , forming satellite states , and undertook rapid economic development which cemented its status as a superpower .
Geopolitical tensions with the United States led to the Cold War . The American-led Western Bloc coalesced into NATO in 1949, prompting the Soviet Union to form its own military alliance, the Warsaw Pact , in 1955. Neither side engaged in direct military confrontation, and instead fought on an ideological basis and through proxy wars . In 1953, following Stalin's death , the Soviet Union undertook a campaign of de-Stalinization under Nikita Khrushchev , which saw reversals and rejections of Stalinist policies. This campaign caused tensions with Communist China . During the 1950s, the Soviet Union expanded its efforts in space exploration and took a lead in the Space Race with the first artificial satellite , the first human spaceflight , the first space station , and the first probe to land on another planet . In 1985, the last Soviet leader, Mikhail Gorbachev , sought to reform the country through his policies of glasnost perestroika overthrew their Soviet-backed regimes , and nationalist and separatist movements erupted across the Soviet Union. In 1991, amid efforts to preserve the country as a renewed federation , an attempted coup against Gorbachev by hardline communists prompted the largest republics—Ukraine, Russia, and Belarus—to secede. On 26 December, Gorbachev officially recognized the dissolution of the Soviet Union . Boris Yeltsin , the leader of the Russian SFSR , oversaw its reconstitution into the Russian Federation , which became the Soviet Union's successor state; all other republics emerged as fully independent post-Soviet states .
During its existence, the Soviet Union produced
many significant social and technological achievements and innovations . It
had the world's second-largest economy and largest standing military. An
NPT-designated state , it wielded the
largest arsenal of nuclear weapons in the world . As an Allied nation, it was a
founding member of the
United Nations as well as one of the
five permanent members of the
United Nations Security Council . Before its dissolution, the Soviet Union was one of the world's two superpowers through its hegemony in Eastern Europe, global diplomatic and ideological influence (particularly in the
Global South ), military and economic strengths, and
scientific accomplishments. (
Full article... )
Entries here consist of Good and Featured articles, which meet a core set of high editorial standards. The background of the Winter War Winter War between Finland and the Soviet Union (1939–1940), which stretches from the Finnish Declaration of Independence in 1917 to the Soviet-Finnish negotiations in 1938–1939.
Before its independence, Finland had been an autonomous grand duchy within Imperial Russia . During the ensuing Finnish Civil War , the Red Guards , supported by the Russian Bolsheviks , were defeated. Fearful of Soviet designs, in the 1920s and the 1930s, the Finns were constantly attempting to align themselves with Scandinavian neutrality, particularly regarding to Sweden . Furthermore, the Finns engaged in secret military co-operation with Estonia in the 1930s. (Full article...
Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Lenin
“
Complete equality of rights for all nations; the right of nations to self-determination; the unity of the workers of all nations—such is the national program that Marxism, the experience of the whole world, and the experience of Russia, teach the workers.
”
The following are images from various Soviet Union-related articles on Wikipedia.
Image 2 Mikhail Gorbachev in one-to-one discussions with US President
Ronald Reagan (
left ), 1985 (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 3 Stalin and
Lavrentiy Beria with Stalin's daughter,
Svetlana , on his lap. As head of the NKVD, Beria was responsible for many
political repressions in the Soviet Union . (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 4 The
Battle of Stalingrad , considered by many historians as a decisive turning point of World War II (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 5 Soviet leader
Nikita Khrushchev (left) with US President
John F. Kennedy in Vienna, 3 June 1961 (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 6 The
Russian famine of 1921–22 killed an estimated 5 million people.
(from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 7 From left to right, the Soviet General Secretary
Joseph Stalin , US President
Franklin D. Roosevelt and British Prime Minister
Winston Churchill confer in Tehran, 1943 (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 8 Forward gun of
Aurora that fired the signal shot (from
October Revolution )
Image 9 Russian troops in trenches awaiting a German attack (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 10 Lenin ,
Trotsky and
Kamenev celebrating the second anniversary of the October Revolution (from
October Revolution )
Image 13 Residents of Leningrad leave their homes destroyed by German bombing. About 1 million civilians died during the 871-day
Siege of Leningrad , mostly from starvation. (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 14 Anniversary of October Revolution in
Riga , Soviet Union in 1988 (from
October Revolution )
Image 15 Lenin ,
Trotsky , and
Kamenev celebrating the second anniversary of the
October Revolution (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 16 Revolutionaries protesting in February 1917 (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 17 Map showing the greatest territorial extent of the Soviet Union and the sovereign states that it dominated politically, economically and militarily in 1960, after the
Cuban Revolution of 1959 but before the official
Sino-Soviet split of 1961 (total area: c. 35,000,000 km
2 ) (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 18 The
Pan-European Picnic took place in August 1989 on the Hungarian-Austrian border. (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 19 The elections to the
Constituent Assembly took place in November 1917. The Bolsheviks won 24% of the vote. (from
October Revolution )
Image 20 The New York Times headline from 9 November 1917 (from
October Revolution )
Image 22 Changes in national boundaries after the end of the Cold War (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 23 Soviet general secretary
Leonid Brezhnev and US President
Jimmy Carter sign the
SALT II arms limitation treaty in Vienna on 18 June 1979. (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 24 Country emblems of the Soviet Republics before and after the dissolution of the Soviet Union (the
Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic (fifth in the second row) no longer exists as a political entity of any kind and the emblem is unofficial.) (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 25 Petrograd
Milrevcom proclamation about the deposing of the
Russian Provisional Government (from
October Revolution )
Image 26 Russian Civil War in the European part of Russia (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 27 Internally displaced Azerbaijanis from
Nagorno-Karabakh , 1993 (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 28 Russian troops meeting German troops in No Man's Land (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 29 Soldiers marching in
Petrograd , March 1917 (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 30 The dissolution of the Constituent Assembly on 6 January 1918. The
Tauride Palace is locked and guarded by
Trotsky ,
Sverdlov ,
Zinoviev , and
Lashevich . (from
October Revolution )
Image 31 Murder of the Romanov family,
Le Petit Journal (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 33 Revolutionaries attacking the tsarist police in the early days of the February Revolution (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 35 On 21 December 1991, the leaders of 11 former Soviet republics, including Russia and Ukraine, agreed to the
Alma-Ata Protocols , formally establishing the
Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). (from
History of the Soviet Union )
Image 36 American, British, and Japanese Troops parade through Vladivostok in armed support to the White Army. (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 37 "Pogrom in the Winter Palace" by
Ivan Vladimirov (from
October Revolution )
Image 38 A revolutionary meeting of Russian soldiers in March 1917 in Dalkarby of
Jomala ,
Åland (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 40 Meeting before the Russian wire entanglements (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 41 A scene from the July Days. The army has just opened fire on street protesters. (from
October Revolution )
Image 42 Red Guard unit of the Vulkan factory in Petrograd, October 1917 (from
October Revolution )
Image 43 Bolshevik (1920) by
Boris Kustodiev (from
October Revolution )
Image 44 European theatre of the
Russian Civil War in 1918 (from
October Revolution )
Image 45 The 2nd Moscow Women Death Battalion protecting the Winter Palace as the last guards of the stronghold (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 46 Provisional Government 's volunteer soldiers secure Petrograd's
Palace Square with the
Austin Armoured Car , summer 1917. (from
Russian Revolution )
Image 47 The dissolution of the
Constituent Assembly on 6 January 1918. The
Tauride Palace is locked and guarded by
Trotsky ,
Sverdlov ,
Zinoviev and
Lashevich . (from
Russian Revolution )
Selected anniversaries for February
Soviet Army Day Red Army in February 1918. Unlike others, it was not an official holiday.
(auto generated)
This is a list of recognized content, updated weekly by JL-Bot (talk · contribs ) (typically on Saturdays). There is no need to edit the list yourself. If an article is missing from the list, make sure it is tagged (e.g. {{ WikiProject Soviet Union }} ) or categorized correctly and wait for the next update. See WP:RECOG for configuration options.
2020-09-16 165855 Soviet submarine B-515
Alexei Leonov
Field Marshall Keitel signs German surrender terms in Berlin 8 May 1945 - Restoration
German instrument of surrender2
Instrument of surrender Japan2
Mamoru Shigemitsu signs the Instrument of Surrender, officially ending the Second World War
Maxim Gorky LOC Restored edit1
Moscow Elektrozavodskaya metro station asv2018-09
Prokofieff (i.e. Prokofiev) LCCN2014708419 Crop 2
RUS-2016-Murmansk-Icebreaker Lenin 01
Raising a flag over the Reichstag - Restoration
Russian Imperial Family 1913
USS Yorktown collision
Yalta Conference (Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin) (B&W)
Yuri Gagarin (1961) - Restoration
Yury Pen - Portrait of Marc Chagall
Did you know? articles
Main page featured articles
Main page featured lists
German instrument of surrender2 (2009-05-07)
Instrument of surrender Japan2 (2009-09-02)
Yalta Conference (Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin) (B&W) (2010-05-08)
USS Yorktown collision (2011-02-12)
Maxim Gorky LOC Restored edit1 (2013-03-28)
Yuri Gagarin (1961) - Restoration (2020-03-09)
Alexei Leonov (2020-03-18)
Field Marshall Keitel signs German surrender terms in Berlin 8 May 1945 - Restoration (2020-05-08)
RUS-2016-Murmansk-Icebreaker Lenin 01 (2020-06-08)
Moscow Elektrozavodskaya metro station asv2018-09 (2022-02-26)
Russian Imperial Family 1913 (2022-07-17)
Mamoru Shigemitsu signs the Instrument of Surrender, officially ending the Second World War (2022-09-02)
2020-09-16 165855 Soviet submarine B-515 (2023-04-18)
Prokofieff (i.e. Prokofiev) LCCN2014708419 Crop 2 (2023-07-25)
Raising a flag over the Reichstag - Restoration (2025-05-02)
Category puzzle Select [►] to view subcategories
Привет Wikipedia is the encyclopedia that anyone can edit. If you are interested in the Soviet Union and have some information that can be added to an existing article, please help. Here are some things you can do:
General: Portals: Tools: Task forces Task forces Related projects: Project-specific guidelines:
Purge server cache