
Back Portal:Schwiiz ALS بوابة:سويسرا Arabic دەروازە:سویس CKB Portál:Švýcarsko Czech Portal:Schweiz German Portalo:Svislando Esperanto Portal:Suiza Spanish Portail:Suisse French Portal:Suíza Galician Portale:Svizzera Italian
The Switzerland Portal



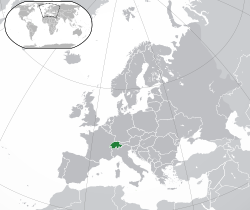
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland is geographically divided among the Swiss Plateau, the Alps and the Jura; the Alps occupy the greater part of the territory, whereas most of the country's 9 million people are concentrated on the plateau, which hosts its largest cities and economic centres, including Zurich, Geneva, and Lausanne.
Switzerland is a federal republic composed of 26 cantons, with federal authorities based in Bern. It has four main linguistic and cultural regions: German, French, Italian and Romansh. Although most Swiss are German-speaking, national identity is fairly cohesive, being rooted in a common historical background, shared values such as federalism and direct democracy, and Alpine symbolism. Swiss identity transcends language, ethnicity, and religion, leading to Switzerland being described as a Willensnation ("nation of volition") rather than a nation state.
Switzerland originates from the Old Swiss Confederacy established in the Late Middle Ages as a defensive and commercial alliance; the Federal Charter of 1291 is considered the country's founding document. The confederation steadily expanded and consolidated despite external threats and internal political and religious strife. Swiss independence from the Holy Roman Empire was formally recognised in the Peace of Westphalia in 1648. The confederation was among the first and few republics of the early modern period, and the only one besides San Marino to survive the Napoleonic Wars.
Switzerland remained a network of self-governing states until 1798, when revolutionary France invaded and imposed the centralist Helvetic Republic. Napoleon abolished the republic in 1803 and reinstated a confederation. Following the Napoleonic Wars, Switzerland restored its pre-revolutionary system, but by 1830 faced growing division and conflict between liberal and conservative movements; this culminated in a new constitution in 1848 that established the current federal system and enshrined principles such as individual rights, separation of powers, and parliamentary bicameralism. (Full article...)
Nico Hischier (born 4 January 1999) is a Swiss professional ice hockey centre and captain of the New Jersey Devils of the National Hockey League (NHL). Hischier made his professional debut in his native Switzerland in 2015, spending time both in the top-tier National League A (NLA) and the second-tier National League B. He moved to North America for the 2016–17 season to play major junior hockey for the Halifax Mooseheads of the Quebec Major Junior Hockey League (QMJHL) in hopes of furthering his hockey career; in his first season in the QMJHL, he was named rookie of the year, along with the award for best rookie in the Canadian Hockey League (CHL), the governing body for major junior hockey in Canada. Internationally Hischier has represented Switzerland at several junior tournaments, including two World Junior Championships. Regarded as a strong two-way forward and a top prospect for the 2017 NHL entry draft, Hischier was selected first overall by the Devils, the first time a Swiss player was selected first overall, and made his NHL debut in 2017. He was named captain of the Devils in 2021. (Full article...)
Selected article -

The Sonderbund War (German: Sonderbundskrieg, French: Guerre du Sonderbund, Italian: Guerra del Sonderbund) of November 1847 was a civil war in Switzerland, then still a relatively loose confederacy of cantons. It ensued after seven Catholic cantons formed the Sonderbund ("separate alliance") in 1845 to protect their interests against a centralization of power. The war concluded with the defeat of the Sonderbund. It resulted in the emergence of Switzerland as a federal state, concluding the period of political "restoration and regeneration" in Switzerland.
The Sonderbund consisted of the cantons of Lucerne, Fribourg, Valais, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden and Zug, all predominantly Catholic and governed by conservative administrations. The cantons of Ticino and Solothurn, also predominantly Catholic but governed by liberal administrations, did not join the alliance. (Full article...)
General images -
The Battle of Winterthur (27 May 1799) was an important action between elements of the Army of the Danube and elements of the Habsburg army, commanded by Friedrich Freiherr von Hotze, during the War of the Second Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The small town of Winterthur lies 18 kilometers (11 mi) northeast of Zürich, in Switzerland. Because of its position at the junction of seven roads, the army that held the town controlled access to most of Switzerland and points crossing the Rhine into southern Germany. Although the forces involved were small, the ability of the Austrians to sustain their 11-hour assault on the French line resulted in the consolidation of three Austrian forces on the plateau north of Zürich, leading to the French defeat a few days later.
By mid-May 1799, the Austrians had wrested control of parts of Switzerland from the French as forces under the command of Hotze and Count Heinrich von Bellegarde pushed them out of the Grisons. After defeating Jean-Baptiste Jourdan's 25,000-man Army of the Danube at the battles of Ostrach and Stockach, the main Austrian army, under command of Archduke Charles, crossed the Rhine at the Swiss town of Schaffhausen and prepared to unite with the armies of Hotze and Friedrich Joseph, Count of Nauendorf, on the plains surrounding Zürich. (Full article...)
List of Featured articles
|
|---|
Selected picture -
Related portals
Switzerland-related topics
New articles
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2025-05-07 00:04 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Vanessa Gentile (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dr. Molly Lee (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 17
- Anna Erat (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dr. Molly Lee (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 51
- Indian Trails Conference (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moserjames79 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 16
- Sarajevo Holiday Market (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PeppermintSA (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 12
- 2025 FIFA Youth Series (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kezyfooty (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 62
- 20th Locarno Film Festival (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SquawkGuard (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 45
- DC Racing Solutions (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SteeledDock541 (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-06, score: 70
- Iron Dames (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SteeledDock541 (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-05, score: 75
- Fontanivent railway station (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Swiss512 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-05, score: 158
- Margaret Rarru Garrawurra (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sethmcolli (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 14
- Un ange frappe à ma porte (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SRamzy (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 24
- Aisha's Story (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bearcat (talk · contribs · new pages (126)) started on 2025-05-05, score: 20
- Victor Yarsley (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DavidGSDavies (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-05, score: 20
- 2024–25 in European women's basketball (L–Z) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ILoveSport2006 (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2025-05-05, score: 41
- Zalman of St. Goar (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AndreJustAndre (talk · contribs · new pages (52)) started on 2025-05-05, score: 14
- 19th Locarno Film Festival (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SquawkGuard (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-05, score: 25
- 2024–25 in Turkish football (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Oltnilhn (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 18
- Who's Crazy? (film) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SquawkGuard (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 32
- Kunio Yasue (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fakt Keaton (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 15
- List of Michelin-starred restaurants in Switzerland (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by History6042 (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 237
- Mike Duggan (Canadian politician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fulserish (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 14
- Zifu Temple (Zhuzhou) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Huangdan2060 (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 38
- 18th Locarno Film Festival (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SquawkGuard (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 52
- 17th Locarno Film Festival (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SquawkGuard (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-05-04, score: 107
- 1961–62 Swiss Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Huligan0 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-05-03, score: 328
- 1962–63 Swiss Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Huligan0 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-05-03, score: 342
- Der Rote Ritter (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Uriahheep228 (talk · contribs · new pages (47)) started on 2025-05-03, score: 36
- KSuite (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gusthes (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-03, score: 20
- 0xCollection (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Superboilles (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-05-03, score: 56
- Cornu (surname) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by QEnigma (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-05-03, score: 20
- André Guillard (footballer) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barr Theo (talk · contribs · new pages (138)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 14
- 1963–64 Swiss Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Huligan0 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 298
- List of Millennial Academy Award winners and nominees (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GeniusTaker (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 14
- Belmore Browne (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Engineerchange (talk · contribs · new pages (20)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 26
- Hertha Sponer Prize (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by de>Mjoppien (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 14
- Iran–United States relations during the Biden administration (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lova Falk (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 13
- Isabelle Chappuis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (301)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 128
- Iran–United States relations during the first Trump administration (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lova Falk (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 13
- Iran–United States relations during the Obama administration (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lova Falk (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 19
- Andrey Viktorovich Burmistrov (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Olga Pachulia (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 17
- László Harsányi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SuperSkaterDude45 (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2025-05-02, score: 30
- FK Bodø/Glimt in European football (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cakebos12 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-01, score: 11
- Geneva school (literary criticism) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 许岚珊 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-05-01, score: 44
- David Thomas (Ohio politician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Nahida (talk · contribs · new pages (27)) started on 2025-05-01, score: 12
- Alessandro Romano (footballer, born 2006) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Das osmnezz (talk · contribs · new pages (32)) started on 2025-05-01, score: 81
- Giancarlo Devasini (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Afus199620 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2025-05-01, score: 43
- Déjà vu (2001 film) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DareshMohan (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2025-05-01, score: 14
- Longshan Temple (Zhuzhou) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Huangdan2060 (talk · contribs · new pages (18)) started on 2025-05-01, score: 38
- Ocean Independence (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Superboilles (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 54
- Julia Ris (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Superboilles (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 78
- Lake Verde (Parma) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Luizadnts (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 38
- Lake Pantano d'Avio (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Luizadnts (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 38
- Lake Moo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Luizadnts (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 38
- Rietmann family (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Superboilles (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 143
- List of mayors of Canton, Ohio (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by M2545 (talk · contribs · new pages (54)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 12
- Dussaud (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barr Theo (talk · contribs · new pages (138)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 20
- Derek Pratt (watchmaker) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AstrooKai (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 18
- Unblu (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Silverstone2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 60
- List of ambassadors of Russia to Switzerland (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Spokoyni (talk · contribs · new pages (35)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 136
- Duilio (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sims2aholic8 (talk · contribs · new pages (35)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 40
- Joel Roth (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barr Theo (talk · contribs · new pages (138)) started on 2025-04-30, score: 20
- 1964–65 Swiss Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Huligan0 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 318
- ACentauri Solar Racing (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Adam79689 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 78
- Cantón El Sunza (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SanSalvador503 (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2025-04-29, score: 12
- Egon Gstöhl (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheBritinator (talk · contribs · new pages (37)) started on 2025-04-28, score: 36
- David B. Berkowitz (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kitsu23 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-28, score: 14
- Dave Phillips (musician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rcarlberg (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-28, score: 50
- Bicentenary of the death of Napoleon I (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WormEater13 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-04-28, score: 20
- Ryan Bergert (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Malmmf (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-04-27, score: 12
- 1954 World Men's Handball Championship squads (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Malo95 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-04-27, score: 13
- The New Gospel (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cavarrone (talk · contribs · new pages (38)) started on 2025-04-27, score: 40
- SwissP Defence (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Toadspike (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2025-04-27, score: 75
- 16th Locarno Film Festival (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SquawkGuard (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-04-27, score: 35
- Yurii Morachevskyi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Максим Огородник (talk · contribs · new pages (35)) started on 2025-04-27, score: 32
- Je me sens si seul (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ieslie (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-26, score: 39
- Leila Wandeler (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ProudWatermelon (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-04-26, score: 62
- 1965–66 Swiss Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Huligan0 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-04-26, score: 282
- 1967–68 Swiss Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Huligan0 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-04-26, score: 302
- Edmond Bailly (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Barr Theo (talk · contribs · new pages (138)) started on 2025-04-26, score: 20
- 2025 Geneva Open (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yimingbao (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2025-04-26, score: 41
- Jan Vermant (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mads Rivers (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2025-04-26, score: 17
- Nicholas Omonuk (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jada sttwisar (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-26, score: 17
- Swiss School Of Business Research (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Martha-Lisa Rothschild (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-04-25, score: 82
- 1968–69 Swiss Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Huligan0 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-04-25, score: 286
- Covers.com (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kniepert (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-04-25, score: 16
- 2025 Tour de Romandie (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Martijnvdam97 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2025-04-25, score: 86
- Villars Basket (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Timd21 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2025-04-25, score: 40
- MiHKAL (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AlyInWikiWonderland (talk · contribs · new pages (119)) started on 2025-04-24, score: 82
- Vên (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Deceiverdeceiver (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2025-04-24, score: 26
- Maria Ernestine Walsh-Held (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HangingSwordAlley (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2025-04-24, score: 58
- Jessica Jaccoud (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (301)) started on 2025-04-24, score: 165
- Isabelle Chassot (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (301)) started on 2025-04-24, score: 128
- Philipp Elkuch (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheBritinator (talk · contribs · new pages (37)) started on 2025-04-24, score: 20
- Mike Wood (business executive) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ErktheBerserker (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-23, score: 40
- KCAP (design firm) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bouw1672kroniek (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2025-04-23, score: 34
- Šimek (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by FromCzech (talk · contribs · new pages (36)) started on 2025-04-23, score: 20
- Künzle (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jonathan1 (talk · contribs · new pages (20)) started on 2025-04-23, score: 20
- Künzli (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jonathan1 (talk · contribs · new pages (20)) started on 2025-04-23, score: 20
- O'Bros (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fixer88 (talk · contribs · new pages (53)) started on 2025-04-23, score: 11
- Baisaran Valley (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Curvasingh (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-23, score: 30
- Lorena Fries (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Carigval.97 (talk · contribs · new pages (37)) started on 2025-04-22, score: 34
- Allison Pantuso (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 24Anonymous (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2025-04-22, score: 70
- Matt Svanson (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stonecold415 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2025-04-22, score: 20
- Ernst-Ulrich Petersmann (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robinsonodora (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2025-04-22, score: 14
- Taiwan International Cello Festival (TWICF) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wikisposer (talk · contribs · new pages (0)) started on 2025-04-20, score: 27
WikiProject

Things you can do
- Visit the German-speaking Wikipedians' notice board and help to write, expand and improve Switzerland-related articles
- List newly created articles related to Switzerland
- Suggest Selected article and Selected picture on the list of possible selected articles and pictures
- Help to expand the Switzerland stub articles
- Assist with our Wikiprojects
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



























































