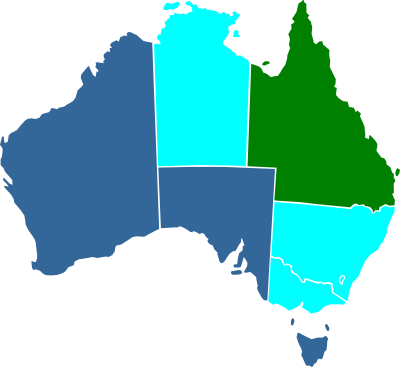
Prostitution in Australia is governed by state and territory laws, which vary considerably, although none ban the selling of sex itself.
- Tasmania, Western Australia and South Australia operate under an abolitionism framework, where the selling of sex itself is not illegal, but activities such as keeping brothels and pimping are illegal.[1][2][3][4]
- The Australian Capital Territory operates under a legalisation framework, where sex work is legal, but brothels must be licensed and can face criminal penalties for operating without a license. Private sex work is legal if the sex worker is working alone.[1][5]
- The Northern Territory, New South Wales, Queensland and Victoria operate under a decriminalisation framework, where most criminal penalties associated with sex work have been removed and brothels or prostitutes are not required to be licensed, however all jurisdictions still have some remaining regulations in regards to where prostitutes or brothels can operate, or on other activities such as advertising.[1][6][7][8][9]
There is no evidence of pre-colonial prostitution amongst Indigenous Australians, however sexual practices more consistent with the modern understanding of polygamy were common, such as the exchange of women to demonstrate friendship. Colonial-era prostitution was controlled via legislation such as the colonial versions of the Contagious Diseases Acts, passed in Victoria and Queensland. Although colonies such as South Australia chose not to pass any CD Act, seeing it as "infringement on the rights of women and official condoning of immorality".[10] After Federation, criminal law was left in the hands of the states, which by and large did not make selling of sex itself illegal, although many acts associated with it such as solicitation, brothel keeping, and leasing accommodations were made illegal.[11]
From the 1970s onwards, prostitution restrictions have generally eased. A 1990 Australian Institute of Criminology report recommended decriminalization of prostitution.[12] New South Wales decriminalized street-based sex work in 1979, using a model subsequently adopted by jurisdictions such as New Zealand, and made brothels legal in 1995.[13]
The United Nations Programme on HIV and AIDS (UNAIDS), which issues regular statistics on sex work, estimated there were around 20,500 sex workers in Australia in 2016.[14] Scarlet Alliance, a national peer sex worker NGO, provides advocacy for sex workers in Australia.
Queensland since 2 August 2024[15] is the most recent state to decriminalise sex work, removing most criminal penalties associated with sex work and abolishing the brothel licensing systems.[16][17][18] Victoria decriminalised sex work in 2023.[19] The Northern Territory decriminalised sex work in 2019.[20]
- ^ a b c "The Legal Status of Sex Work Across Australia". Sydney Criminal Lawyers. 1 May 2023. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
- ^ "Tasmania sex work laws | Scarlet Alliance". scarletalliance.org.au. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ "Western Australia sex work laws | Scarlet Alliance". scarletalliance.org.au. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ "South Australia sex work laws | Scarlet Alliance". scarletalliance.org.au. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ "Australian Capital Territory sex work laws | Scarlet Alliance". scarletalliance.org.au. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ "Northern Territory sex work laws | Scarlet Alliance". scarletalliance.org.au. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ "New South Wales sex work laws | Scarlet Alliance". scarletalliance.org.au. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ "Queensland sex work laws | Scarlet Alliance". scarletalliance.org.au. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ "Victoria's sex work laws | Scarlet Alliance". scarletalliance.org.au. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ Frances 1994.
- ^ Carpenter & Hayes 2014.
- ^ Pinto et al 1990.
- ^ Aroney, Eurydice; Crofts, Penny (30 April 2019). "How Sex Worker Activism Influenced the Decriminalisation of Sex Work in NSW, Australia". International Journal for Crime, Justice and Social Democracy. 8 (2): 50–67. doi:10.5204/ijcjsd.v8i2.955. hdl:10453/133742. ISSN 2202-8005.
- ^ UNData 2019.
- ^ "View - Queensland Legislation - Queensland Government".
- ^ Messenger, Andrew (2 May 2024). "Sex work decriminalised in Queensland after decades of campaigning". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ^ Parliament of Queensland. "Report No. 4, 57th Parliament - Criminal Code (Decriminalising Sex Work) and Other Legislation Amendment Bill 2024". www.parliament.qld.gov.au. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
- ^ Prostitution Licensing Authority (28 April 2023). "Sex Work Industry Review". Retrieved 17 April 2024.
- ^ "Decriminalising sex work in Victoria | Victorian Government". www.vic.gov.au. Retrieved 20 September 2023.
- ^ "NT Parliament votes to decriminalise sex work". ABC News. 26 November 2019. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
