
Back ملاحة لاسلكية Arabic Radioayuda AST Radionavigation Danish Funknavigation German Ραδιοναυτιλία Greek Radioayuda Spanish Raadionavigatsioon Estonian ناوبری رادیویی Persian Radionavigation French Radionavigazione Italian
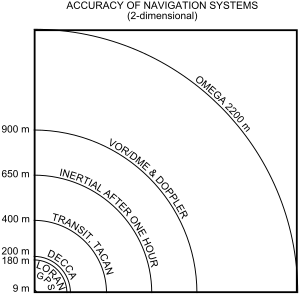
Radio navigation or radionavigation is the application of radio waves to determine a position of an object on the Earth, either the vessel or an obstruction.[1][2] Like radiolocation, it is a type of radiodetermination.
The basic principles are measurements from/to electric beacons, especially
- Angular directions, e.g. by bearing, radio phases or interferometry,
- Distances, e.g. ranging by measurement of time of flight between one transmitter and multiple receivers or vice versa,
- Distance differences by measurement of times of arrival of signals from one transmitter to multiple receivers or vice versa
- Partly also velocity, e.g. by means of radio Doppler shift.[citation needed]
Combinations of these measurement principles also are important—e.g., many radars measure range and azimuth of a target.[citation needed]
- ^ Dutton, Benjamin (2004). "15 – Basic Radio Navigation". Dutton's Nautical Navigation (15 ed.). Naval Institute Press. pp. 154–163. ISBN 155750248X.
- ^ Kayton, Myron; Walter R. Fried (1997). "4 – Terrestrial Radio-Navigation Systems". Avionics Navigation Systems. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 99–177.