Sheikhdom of Diriyah مشيخة الدرعية | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1446–1744 | |||||||||
|
Probable banner | |||||||||
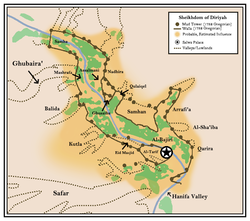 The historical city of Diriyah with estimated traditional extent of the sheikhdom | |||||||||
| Capital | Salwa Palace | ||||||||
| Common languages | Arabic | ||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Dir'iyy | ||||||||
| Sheikh | |||||||||
• 1446–1463 | Mani' bin Rabia | ||||||||
• 1727–1744 | Muhammad bin Saud | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Migration of Mane' bin Rabi'a and his clan | 1446 | ||||||||
| 1744 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Saudi Arabia | ||||||||
The Sheikhdom of Dir'iyah (Arabic: مشيخة الدرعية), was a polity in central Arabia from 1446 to 1744 and the predecessor to the First Saudi State. Its capital was Al-Turaif District, and it was based around the banks of Wadi Hanifa. It was ruled by the Muani'a dynasty (also known as the Marada) from the Durou' clan, and later under its two branches, Muqrin and Watban, with the former becoming the sole house and the house from which the House of Saud descends.

