
Back Einheitsstaat ALS دولة مركزية Arabic Estáu unitariu AST Unitar dövlət Azerbaijani Унитар дәүләт Bashkir Унітарная дзяржава Byelorussian Унітарная дзяржава BE-X-OLD Унитарна държава Bulgarian এককেন্দ্রিক রাষ্ট্র Bengali/Bangla Unitarna država BS
| Part of the Politics series |
| Basic forms of government |
|---|
| List of countries by system of government |
|
|
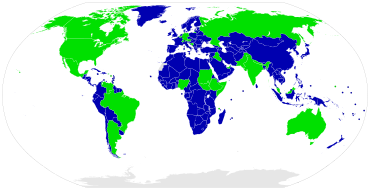
A unitary state is a (sovereign) state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create or abolish administrative divisions (sub-national or sub state units). Such units exercise only the powers that the central government chooses to delegate. Although political power may be delegated through devolution to regional or local governments by statute, the central government may alter the statute, to override the decisions of devolved governments or expand their powers.
The modern unitary state concept originated in France; in the aftermath of the Hundred Years' War, national feelings that emerged from the war unified France. The war accelerated the process of transforming France from a feudal monarchy to a unitary state. The French then later spread unitary states by conquests, throughout Europe during and after the Napoleonic Wars, and to the world through the vast French colonial empire.[1] Presently, prefects remain an illustration of the French unitary state system, as the representatives of the State in each department, tasked with upholding central government policies.
Unitary states stand in contrast to federations, also known as federal states. A large majority of the UN member countries, 166 out of 193, have a unitary system of government, while significant population and land mass is under some kind of federation.[2]
- ^ Holmes, Urban T. Jr. & Schutz, Alexander Herman [in German] (1948). A History of the French Language (revised ed.). Columbus, OH: Harold L. Hedrick. p. 61.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Democracy". United Nations. 2015-11-20. Archived from the original on 2021-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-22.