
Back ضفدع الشجر الأمريكي الأخضر Arabic ضفدع الشجر الامريكى الاخضر ARZ Американска зелена дървесна жаба Bulgarian Reineta verda Catalan Hyla cinerea CEB Karolina-Laubfrosch German Hyla cinerea Spanish Hyla cinerea Basque قورباغه درختی سبز آمریکایی Persian Viherlehtisammakko Finnish
| American green tree frog | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Hylidae |
| Genus: | Dryophytes |
| Species: | D. cinereus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Dryophytes cinereus (Schneider, 1799)
| |
| |
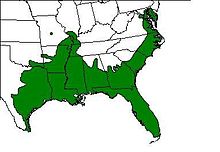
| Approximate range | |
| Synonyms | |
The American green tree frog (Dryophytes cinereus or Hyla cinerea) is a common arboreal species of New World tree frog belonging to the family Hylidae. This nocturnal insectivore is moderately sized and has a bright green to reddish-brown coloration.[2] Commonly found in the central and southeastern United States, the frog lives in open canopy forests with permanent water sources and abundant vegetation.[3][4] The American green tree frog is strictly aquatic during the hibernating and mating seasons.[5] When defending its territory, the frog either emits aggressive call signals or resolves to grapple with intruders, seldom leading to injury or death.[6] To avoid predation, the frog will leap into the water or jump into the treetops.[7]
Females green tree frogs are larger than males. Pairs breed through amplexus.[4] Males emit low frequency advertisement calls to attract females.[8] During mating competition, males will eavesdrop on neighboring rivals and either adjust their signal timing or remain silent to intercept call signals and mate with approaching females.[8][9] Androgens energize males to vocalize.[6]
- ^ IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group (2021). "Dryophytes cinereus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T55449A118978218. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-3.RLTS.T55449A118978218.en. Retrieved 2 December 2022.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Pham-2007was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Suriyamongkol-2021was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
ADWwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Haber, V. R. (April 1926). "The food of the Carolina tree frog, Hyla cinerea Schneider". Journal of Comparative Psychology. 6 (2): 189–220. doi:10.1037/h0073728. ISSN 0093-4127.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Leary-2013was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Gunzburger-2005was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Garcia-2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Perrillwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
