
Back مضلعة Arabic Hať Czech Stammevej Danish Knüppeldamm German جاده الواری Persian Kapulatie Finnish Chemin de rondins French Strada di tronchi Italian Knuppelpad Dutch Kavleveg NN
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2016) |
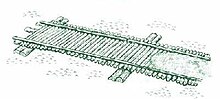


A corduroy road or log road is a type of road or timber trackway made by placing logs, perpendicular to the direction of the road over a low or swampy area. The result is an improvement over impassable mud or dirt roads, yet rough in the best of conditions and a hazard to horses due to shifting loose logs.
Corduroy roads can also be built as a foundation for other surfacing. If the logs are buried in wet, acidic, anaerobic soils such as peat or muskeg, they decay very slowly. A few corduroy road foundations that date back to the early 20th century still exist in North America. One example is the Alaska Highway between Burwash Landing and Koidern, Yukon, Canada, which was rebuilt in 1943, less than a year after the original route was graded on thin soil and vegetation over permafrost, by using corduroy, then building a gravel road on top. During the 1980s, the gravel was covered with a chip-seal. The late 1990s saw replacement of this road with modern road construction, including rerouting of the entire highway.
In World War II corduroyed roads were used by both German and Soviet forces on the Eastern Front.[1]
In slang use, corduroy road can also refer to a road in ill repair, having many potholes, ruts, or surface swellings. This should not be confused with a washboard road.
- ^ Military Improvisations During the Russian Campaign Archived 2013-03-03 at the Wayback Machine, Chap 5, Center of Military History, US Army