
Back الدخل القومي الإجمالي Arabic الدخل القومى ARZ Ümumi milli gəlir Azerbaijani Renda Nacional Bruta Catalan Umumiy içki mahsulat CRH Bruttonationalindkomst Danish Bruttonationaleinkommen German Ακαθάριστο εθνικό εισόδημα Greek Malneta nacia enspezo Esperanto Renta Nacional Bruta Spanish
| Economic sectors |
|---|
| Three-sector model |
|
| Additional sectors |
|
| Theorists |
| Sectors by ownership |
| Grey market |
|---|
| Part of a series on |
| Economic systems |
|---|
|
Major types
|
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign residents, minus income earned in the domestic economy by nonresidents.[2]: 44
Comparing GNI to GDP shows the degree to which a nation's GDP represents domestic or international activity. GNI has gradually replaced GNP in international statistics.[3][4] While being conceptually identical, it is calculated differently.[5] GNI is the basis of calculation of the largest part of contributions to the budget of the European Union.[6] In February 2017, Ireland's GDP became so distorted from the base erosion and profit shifting ("BEPS") tax planning tools of U.S. multinationals, that the Central Bank of Ireland replaced Irish GDP with a new metric, Irish Modified GNI (or "GNI*"). In 2017, Irish GDP was 162% of Irish Modified GNI.[7]
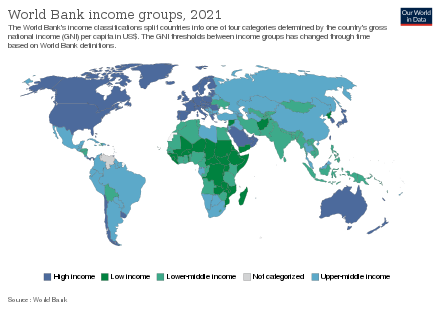
- ^ "World Bank's Income Groups". Our World in Data. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ Todaro, Michael P.; Smith, Stephen C. (2012). Economic development (11 ed.). Addison-Wesley. ISBN 978-0-13-801388-2.
- ^ World Bank. "GNI, Atlas method". data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 2022-10-23.
- ^ World Bank. "GNI, PPP (international $)". data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 2022-10-23.
- ^ "Glossary:Gross national income (GNI)". Eurostat Statistic Explained. Eurostat. Retrieved 2016-06-23.
- ^ "Monitoring GNI for own resource purposes". Eurostat Statistic Explained. Eurostat. Retrieved 2016-06-23.
- ^ Heike Joebges (January 2017). "CRISIS RECOVERY IN A COUNTRY WITH A HIGH PRESENCE OF FOREIGN-OWNED COMPANIES: The Case of Ireland" (PDF). IMK Macroeconomic Policy Institute, Hans-Böckler-Stiftung.