3 Questions: On the future of AI and the mathematical and physical sciences Curiosity-driven research has long sparked technological transformations. A century ago, curiosity about atoms led to quantum mechanics, and eventually the transistor at the heart of modern computing. Conversely, the steam engine was a practical breakthrough, but it took fundamental research ...
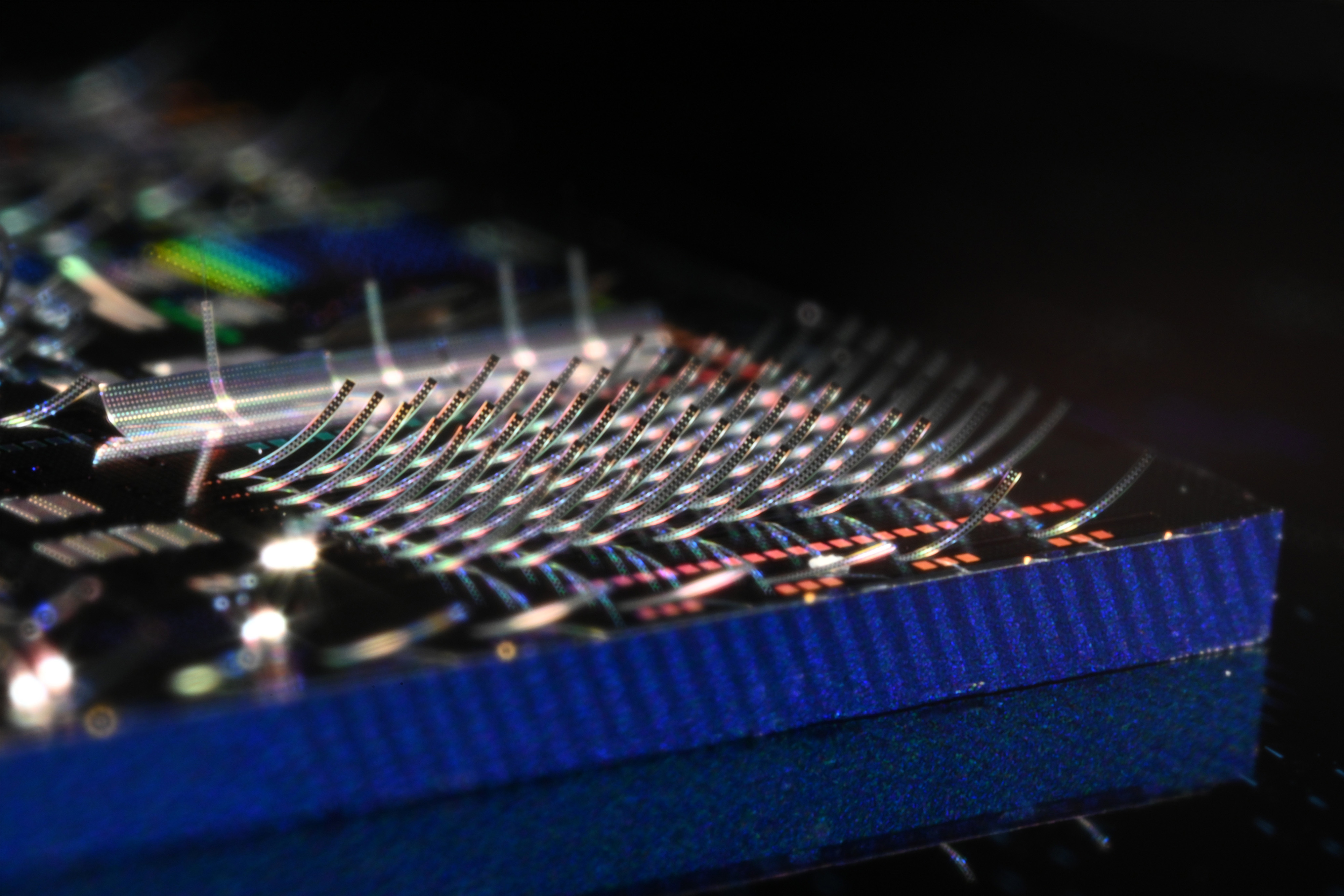
New photonic device efficiently beams light into free space Photonic chips use light to process data instead of electricity, enabling faster communication speeds and greater bandwidth. Most of that light typically stays on the chip, trapped in optical wires, and is difficult to transmit to the outside world in ...
A better method for planning complex visual tasks MIT researchers have developed a generative artificial intelligence-driven approach for planning long-term visual tasks, like robot navigation, that is about twice as effective as some existing techniques.Their method uses a specialized vision-language model to perceive the scenario in an image ...
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink In some parts of the deep ocean, it can look like it’s snowing. This “marine snow” is the dust and detritus that organisms slough off as they die and decompose. Marine snow can fall several kilometers to the deepest parts ...
Neurons receive precisely tailored teaching signals as we learn When we learn a new skill, the brain has to decide — cell by cell — what to change. New research from MIT suggests it can do that with surprising precision, sending targeted feedback to individual neurons so each one ...
Improving AI models’ ability to explain their predictions In high-stakes settings like medical diagnostics, users often want to know what led a computer vision model to make a certain prediction, so they can determine whether to trust its output.Concept bottleneck modeling is one method that enables artificial intelligence ...
X-raying rocks reveals their carbon-storing capacity To avoid the worst effects of climate change, many billions of metric tons of industrially generated carbon dioxide will have to be captured and stored away by the end of this century. One place to store such an enormous amount ...
Seeds of something different In Berlin in the early 1870s, tourists began visiting a neighborhood called Barackia. It did not have museums, palaces, or any other typical attractions. Barackia was a working-class neighborhood where people grew their own food, lived in small dwellings, and ...
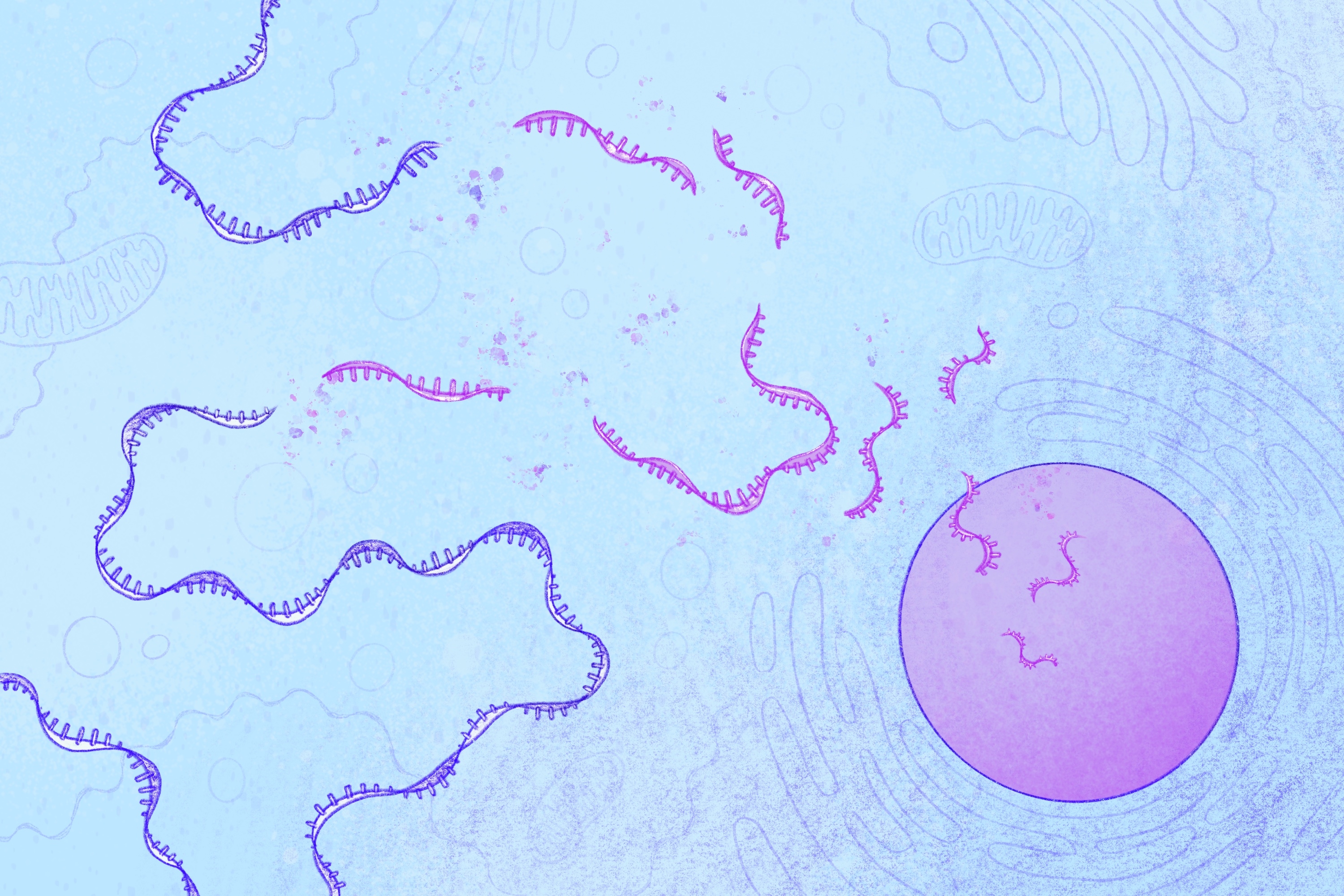
New insights into a hidden process that protects cells from harmful mutations Some genetic mutations that are expected to completely stop a gene from working surprisingly cause only mild or even no symptoms. Researchers in previous studies have discovered one reason why: Cells can ramp up the activity of other genes that ...
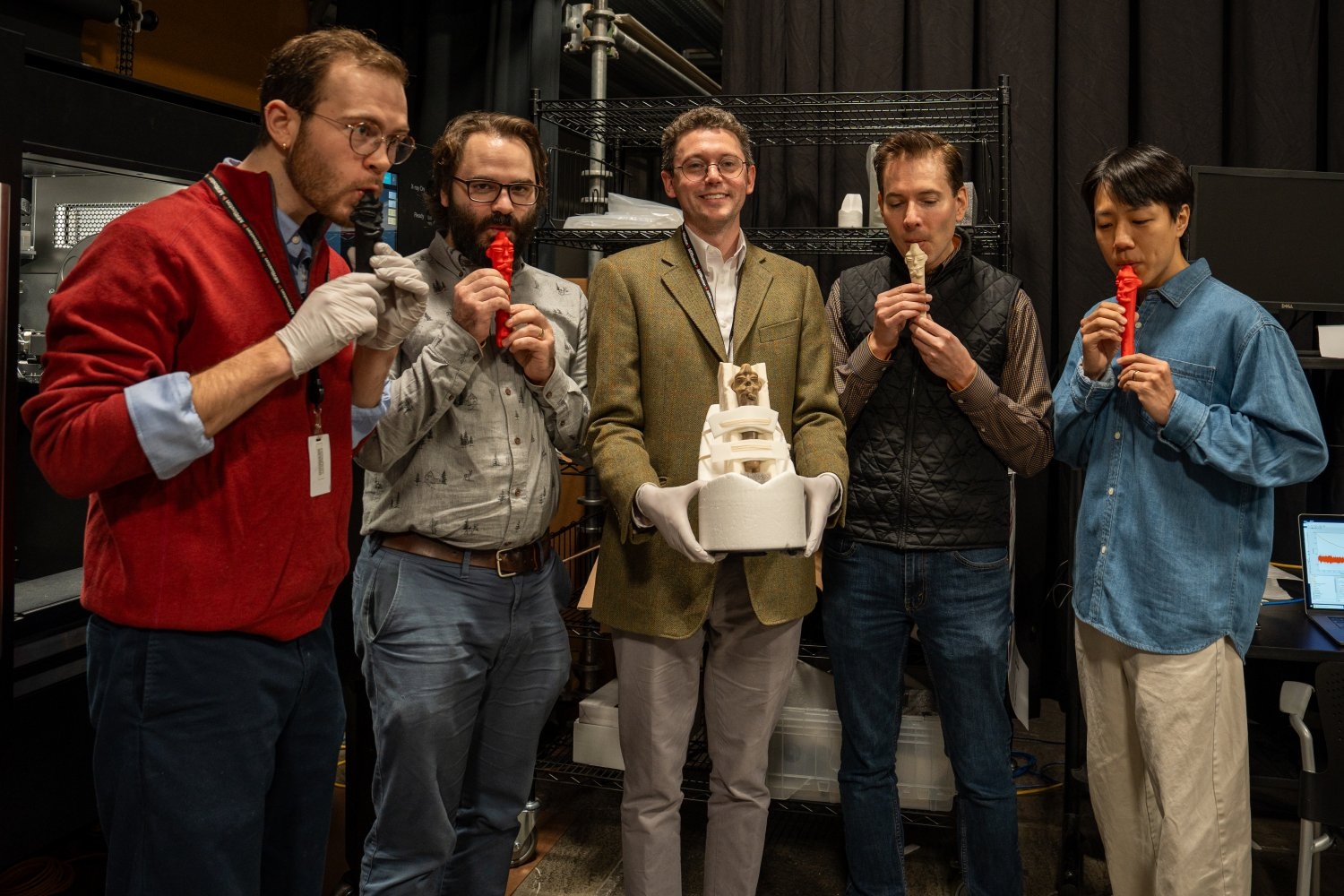
Recreating the forms and sounds of historical musical instruments What if there were a way to create accurate replicas of ancient and historical instruments that could be played and heard? In late 2024, senior MIT postdoc Benjamin Sabatini wrote MIT Professor Eran Egozy to ask just that, and about a ...
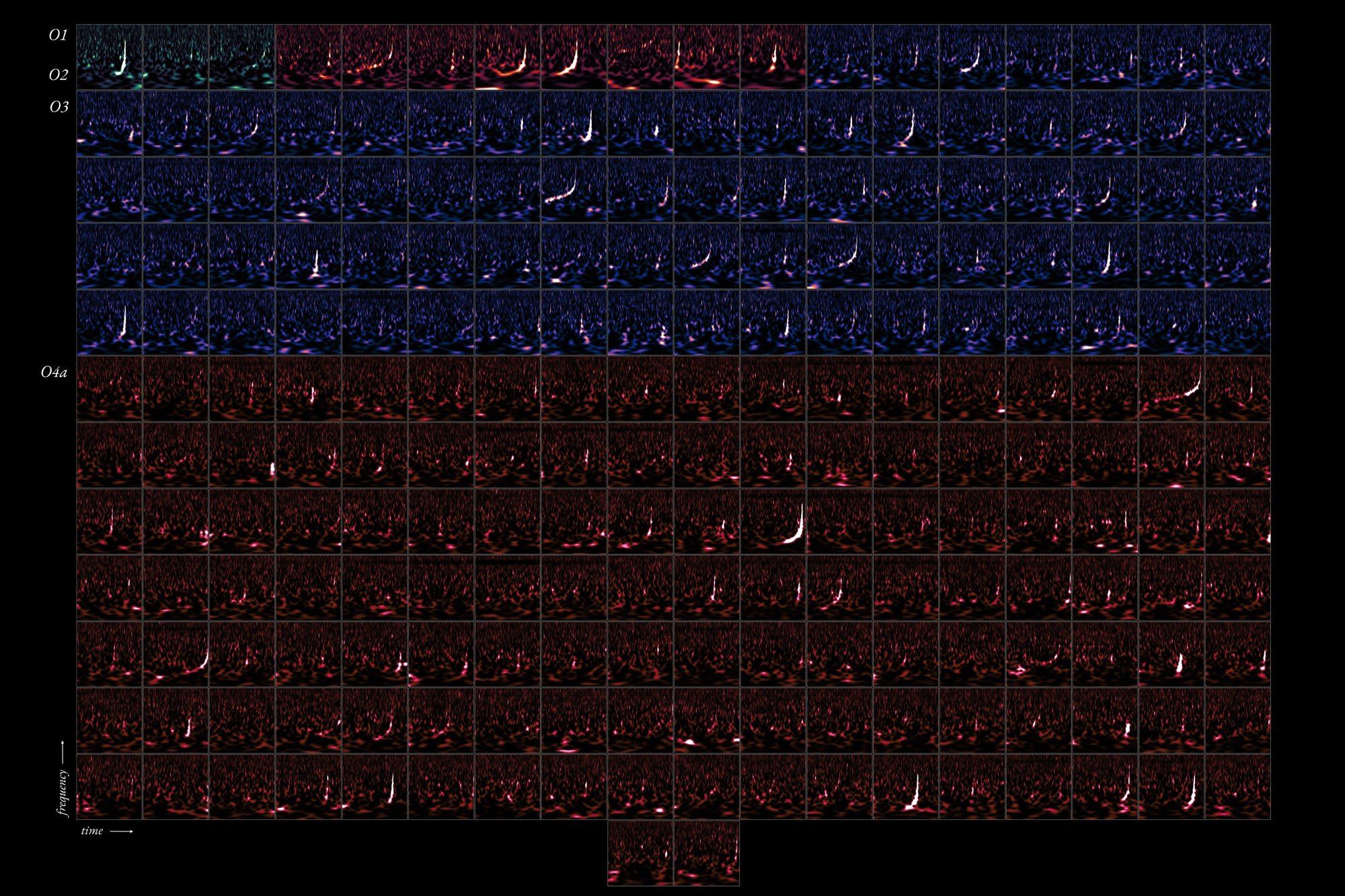
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and... When the densest objects in the universe collide and merge, the violence sets off ripples, in the form of gravitational waves, that reverberate across space and time, over hundreds of millions and even billions of years. By the time they ...
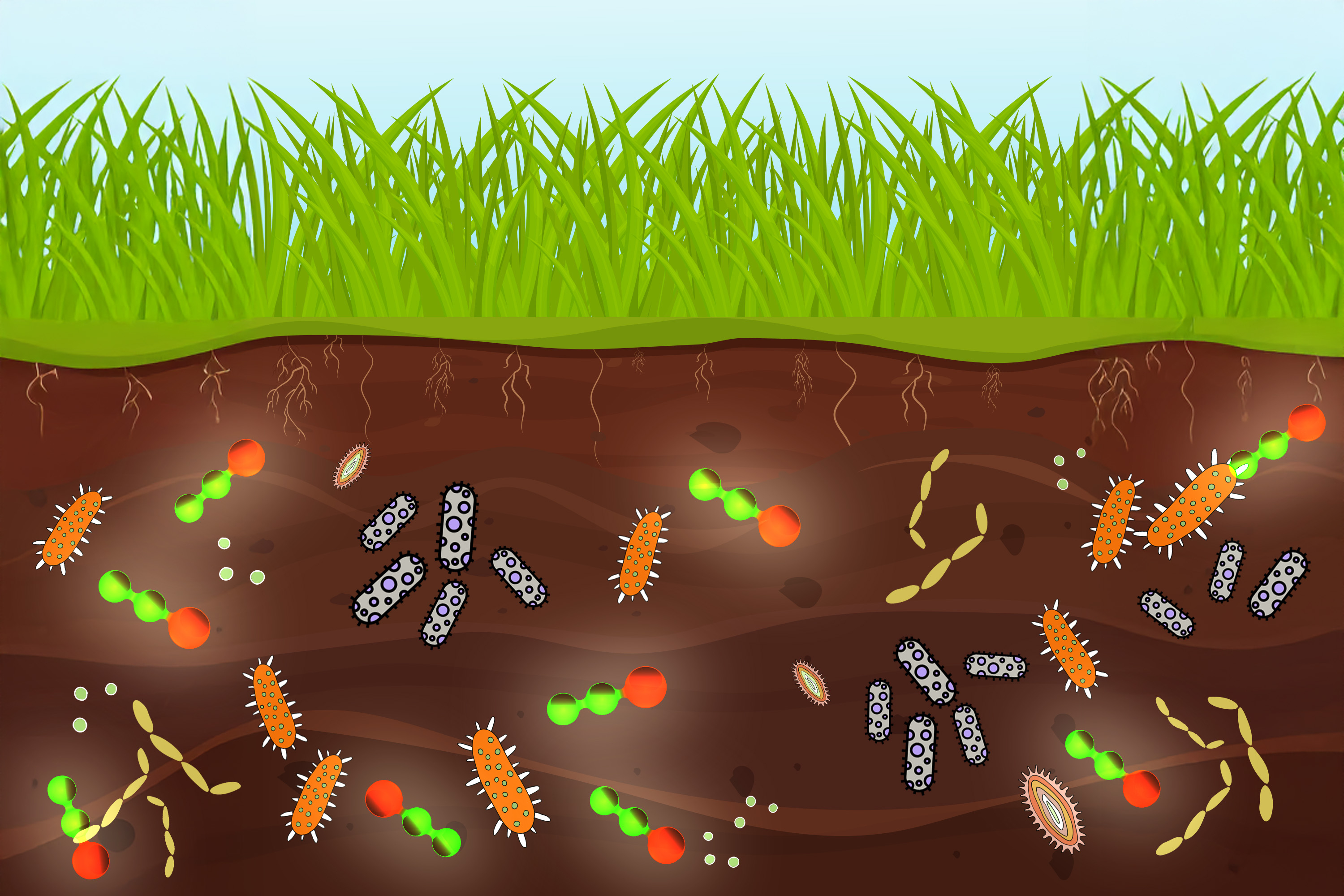
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria Plant growth is supported by millions of tiny soil microbes competing and cooperating with each other as they perform important roles at the plant root, including improving access to nutrients and protecting against pathogens. As a byproduct of their metabolism, ...
A “ChatGPT for spreadsheets” helps solve difficult engineering challenges faster Many engineering challenges come down to the same headache — too many knobs to turn and too few chances to test them. Whether tuning a power grid or designing a safer vehicle, each evaluation can be costly, and there may ...
How some skills become second nature Expertise isn’t easy to pass down. Take riding a bike: A seasoned cyclist might talk a beginner through the basics of how to sit and when to push off. But other skills, like how hard to pedal to keep balanced, ...
Injectable “satellite livers” could offer an alternative to liver transplantation More than 10,000 Americans who suffer from chronic liver disease are on a waitlist for a liver transplant, but there are not enough donated organs for all of those patients. Additionally, many people with liver failure aren’t eligible for a ...
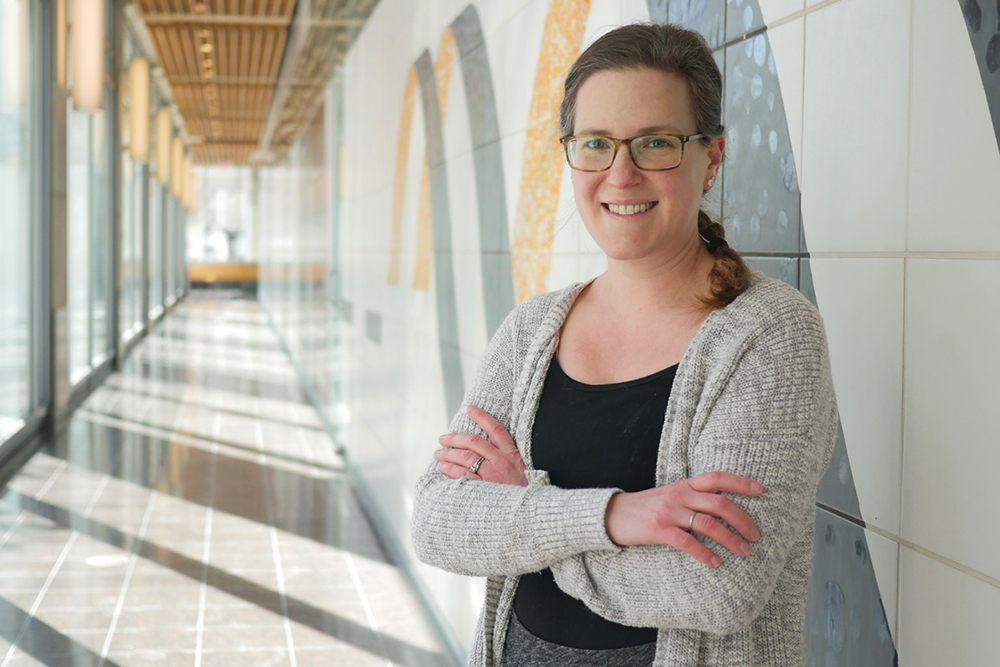
W.M. Keck Foundation to support research on healthy aging at MIT A prestigious grant from the W.M. Keck Foundation to Alison E. Ringel, an MIT assistant professor of biology, will support groundbreaking healthy aging research at the Institute.Ringel, who is also a core member of the Ragon Institute of Mass General ...
Coping with catastrophe Each April in Japan, people participate in a tradition called “hanami,” or cherry-blossom viewing, where they picnic under the blooming trees. The tradition has a second purpose: The presence of people at these gatherings, often by water, helps solidify riverbanks ...
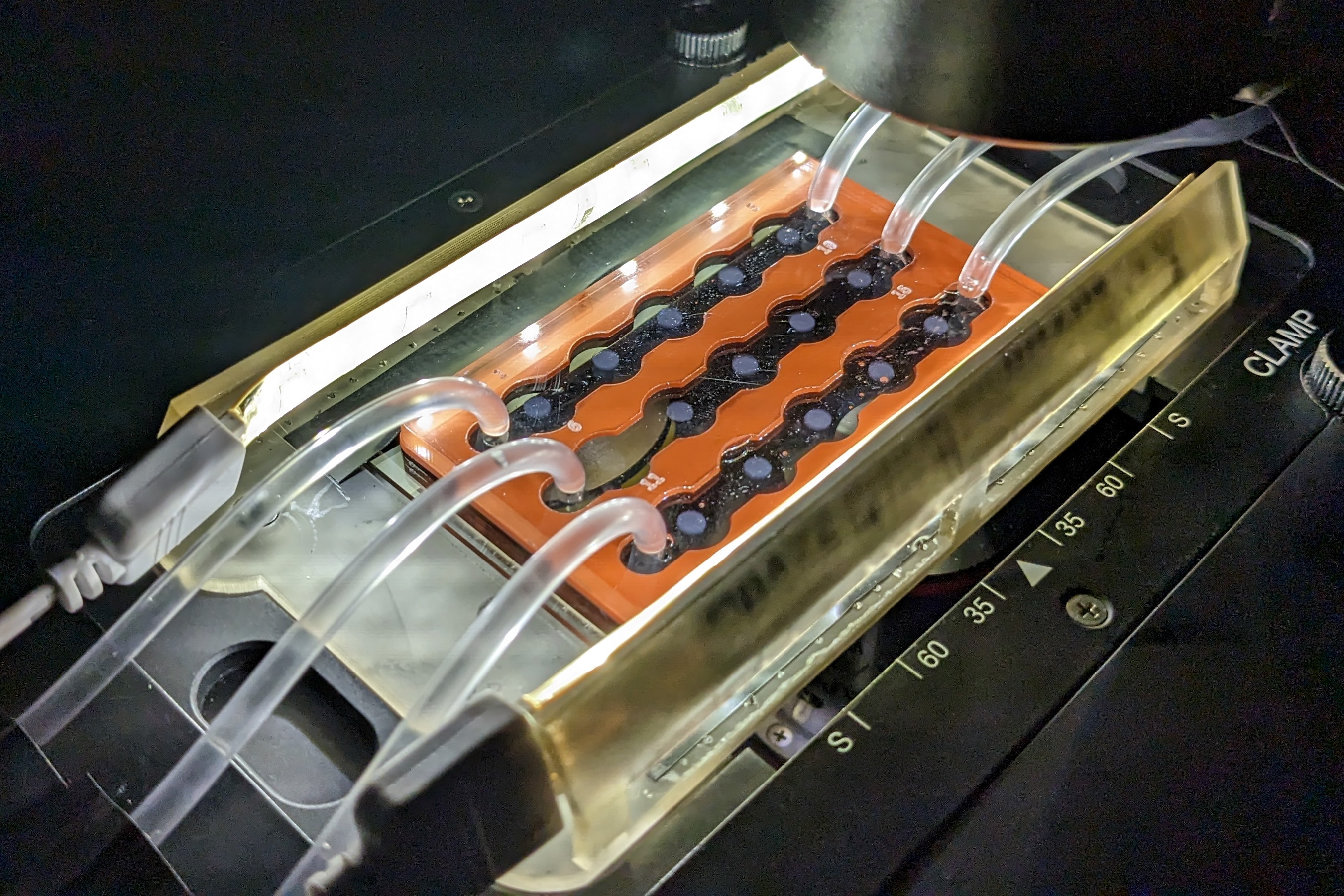
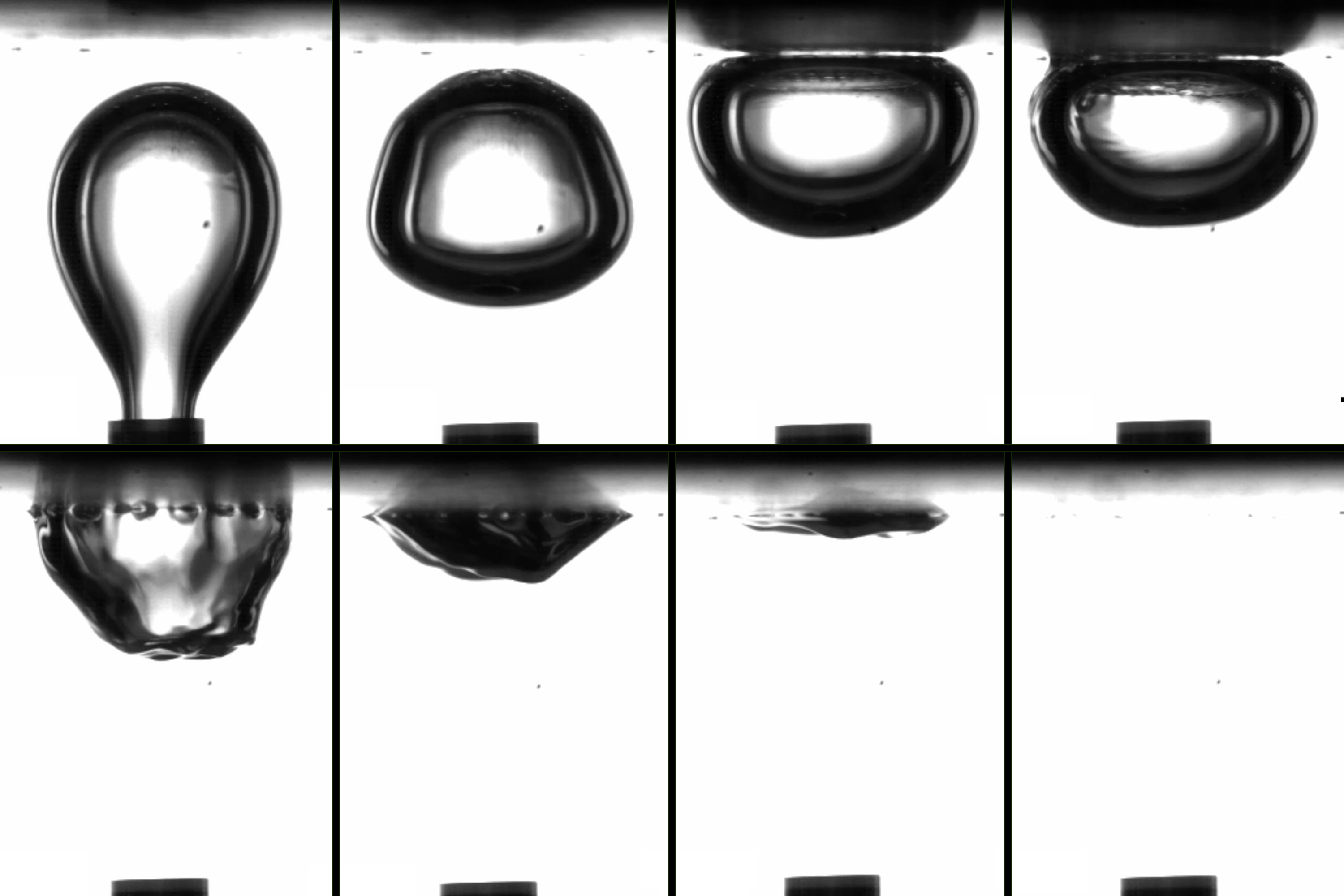
Tackling industry’s burdensome bubble problem In industrial plants around the world, tiny bubbles cause big problems. Bubbles clog filters, disrupt chemical reactions, reduce throughput during biomanufacturing, and can even cause overheating in electronics and nuclear power plants.MIT Professor Kripa Varanasi has long studied methods to ...
New method could increase LLM training efficiency Reasoning large language models (LLMs) are designed to solve complex problems by breaking them down into a series of smaller steps. These powerful models are particularly good at challenging tasks like advanced programming and multistep planning.But developing reasoning models demands ...
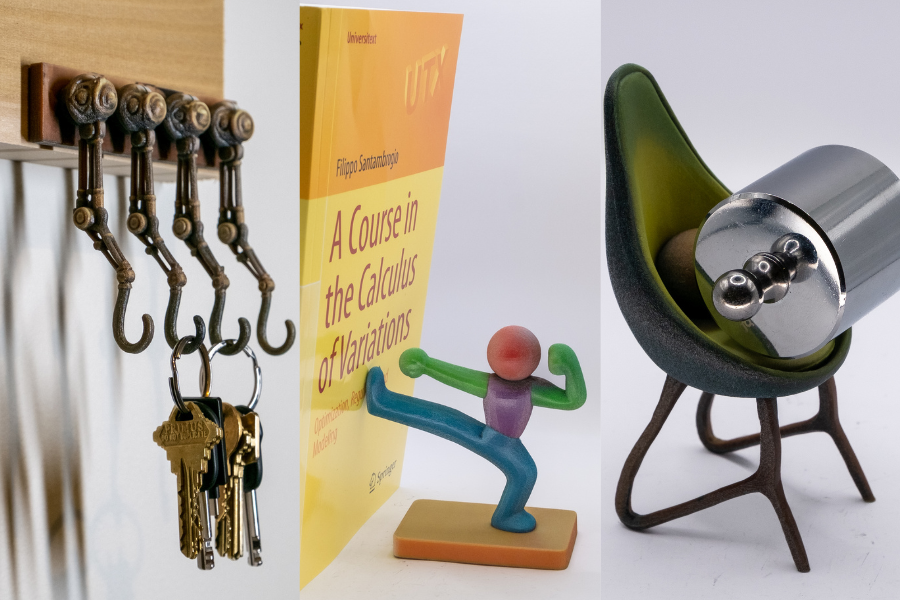
Mixing generative AI with physics to create personal items that work in the real world Have you ever had an idea for something that looked cool, but wouldn’t work well in practice? When it comes to designing things like decor and personal accessories, generative artificial intelligence (genAI) models can relate. They can produce creative and ...
Load More