Back بوابة:الأردن Arabic دەروازە:ئوردن CKB Portail:Jordanie French Պորտալ:Հորդանան Armenian Portal:Jordan Malay Portal:Jordânia Portuguese Портал:Иордания Russian باب:اردن Urdu
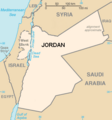
The Jordan Portal  Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and the occupied Palestinian territory of the West Bank and Israel to the west. The Jordan River, flowing into the Dead Sea, is located along the country's western border. Jordan has a small coastline along the Red Sea in its southwest, separated by the Gulf of Aqaba from Egypt. Amman is Jordan's capital and largest city, as well as the most populous city in the Levant. Modern-day Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period. Three kingdoms emerged in Transjordan at the end of the Bronze Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established their kingdom centered in Petra. Later rulers of the Transjordan region include the Assyrian, Babylonian, Roman, Byzantine, Rashidun, Umayyad, Abbasid, and the Ottoman empires. After the Great Arab Revolt against the Ottomans in 1916 during World War I, the Greater Syria region was partitioned by Britain and France. The Emirate of Transjordan was established in 1921 by the Hashemite, then Emir, Abdullah I, and the emirate became a British protectorate. In 1946, Jordan gained independence and became officially known as the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. The country captured and annexed the West Bank during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War until it was occupied by Israel in 1967. Jordan renounced its claim to the territory to the Palestinians in 1988, and signed a peace treaty with Israel in 1994. Jordan is a semi-arid country, covering an area of 89,342 km2 (34,495 sq mi), with a population of 11.5 million, making it the eleventh-most populous Arab country. The dominant majority, or around 95% of the country's population, is Sunni Muslim, with the rest being mostly Arab Christian. Jordan was mostly unscathed by the violence that swept the region following the Arab Spring in 2010. From as early as 1948, Jordan has accepted refugees from multiple neighbouring countries in conflict. An estimated 2.1 million Palestinian (most of whom hold Jordanian citizenship) and 1.4 million Syrian refugees were present in Jordan in 2015. The kingdom is also a refuge for thousands of Christian Iraqis fleeing persecution. While Jordan continues to accept refugees, the large Syrian influx during the 2010s has placed substantial strain on national resources and infrastructure. The sovereign state is a constitutional monarchy, but the king holds wide executive and legislative powers. Jordan is a founding member of the Arab League and the Organisation of Islamic Co-operation. The country has a high Human Development Index, ranking 102nd, and is considered a lower middle income economy. The Jordanian economy, one of the smallest economies in the region, is attractive to foreign investors based upon a skilled workforce. The country is a major tourist destination, also attracting medical tourism due to its well developed health sector. Nonetheless, a lack of natural resources, large flow of refugees, and regional turmoil have hampered economic growth. (Full article...) Selected article -
King Abdullah II Special Forces Group (Arabic: العمليات الخاصة ورد الفعل السريع), commonly known as the JORSOF are strategic-level special forces of the Royal Jordanian Army under the Jordanian Armed Forces. Founded on April 15, 1963, on the orders of the late King Hussein, its primary roles include reconnaissance, counter-terrorism, search and evacuation, intelligence gathering combat, and the protection of key sites. The Special Forces Group are also charged with carrying out precision strikes against critical enemy targets. The unit is equipped and trained to be able to operate behind enemy lines for long periods without any logistical support, and is considered some of the best in the Middle East. (Full article...)
Selected biography -Ali Abu Nuwar (Arabic: علي أبو نوار; surname also spelled Abu Nuwwar, Abu Nawar or Abu Nowar; 1925 – 15 August 1991) was a Jordanian army officer, serving as chief of staff in May 1956 – April 1957. He participated in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War as an artillery officer in the Jordanian army's predecessor, the Arab Legion, but his vocal opposition to British influence in Jordan led to his virtual exile to Paris as military attaché in 1952. There, he forged close ties with Jordanian crown prince Hussein, who promoted Abu Nuwar after his accession to the throne. Abu Nuwar's enmity with Glubb Pasha, the Arab Legion's powerful British chief of staff, his insistence on establishing Arab command over the army and his influence with Hussein led the latter to dismiss Glubb Pasha and appoint Abu Nuwar in his place. However, Abu Nuwar's ardent support for the pan-Arabist policies of Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser contributed to Jordan's increasing isolation from the UK and the US, which were major sources of foreign aid to Jordan. At the same time, existing dissatisfaction with Abu Nuwar's leadership by palace officials and veteran Bedouin army units culminated into violent confrontations at the large army barracks in Zarqa between royalist and Arab nationalist units. Two principal accounts emerged regarding the events at Zarqa, with the royalist version holding that the incident was an abortive coup by Abu Nuwar against Hussein, and the dissident version asserting that it was a staged, American-backed counter-coup by Hussein against the pan-Arabist movement in Jordan. In any case, Abu Nuwar resigned and was allowed to leave Jordan for Syria. He was subsequently sentenced to 15 years in absentia. (Full article...)WikiProjectFor editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Jordan-related articles, see WikiProject Jordan. General images -The following are images from various Jordan-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected city -Al-Karak (Arabic: الكرك) is a city in Jordan known for its medieval castle, the Kerak Castle. The castle is one of the three largest castles in the region, the other two being in Syria. Al-Karak is the capital city of the Karak Governorate. Al-Karak lies 140 kilometres (87 mi) to the south of Amman on the ancient King's Highway. It is situated on a hilltop about 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) above sea level and is surrounded on three sides by a valley. Al-Karak has a view of the Dead Sea. A city of about 32,216 people (2005) has been built up around the castle and it has buildings from the 19th-century Ottoman period. The town is built on a triangular plateau, with the castle at its narrow southern tip. (Full article...)
See also: List of cities in Jordan
Related portalsReligions in Jordan Arab states Other countries Recognized content
Featured articlesGood articles
TopicsSelected topic overview -
CategoriesSelected picture - Credit: Daniel Case Wadi Rum's resemblance to the surface of Mars has made it a popular filming and tourist attraction
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
SourcesDiscover Wikipedia using portals |